All Facilities Created
A comprehensive overview of infrastructure and facilities established across all 29 projects.
Total Facilities
115
Across All Projects
Active Locations
115
Sites Developed
Top Projects by Infrastructure Creation
Top 10
Strengethening of Farm Mechanization unit at KVK Shuhama SKUAST-K, Shalimar
Under SKUAST-Kashmir, Shuhama focuses on agricultural research, frontline demonstrations, and farmer training to promote improved crop production, seed technology, and sustainable farming practices in the region.
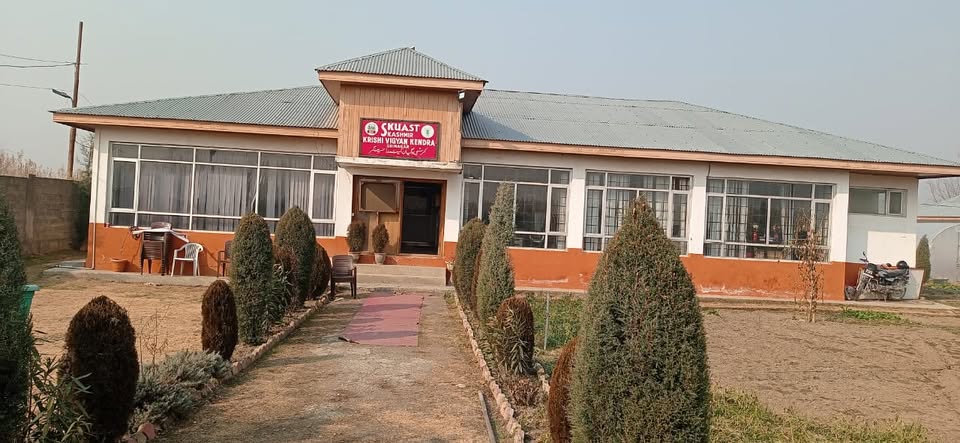

Strengthening of Farm Mechanization unit at KVK-Srinagar SKUAST-K, Shalimar
A frontline agricultural extension center in Srinagar, providing farmers with training, demonstrations, and technology support to improve crop production, livestock, and overall farm productivity.

Strengthening of Seed Research and Farm Machinery Unit DARS, BUDGAM, SKUAST-K, SHALIMAR
The “Strengthening of Seed Research and Farm Machinery Unit” at DARS, Budgam focuses on upgrading research capacity, improving seed-production efficiency, and modernizing farm operations through the introduction of advanced machinery and scientific tools. The initiative aims to enhance breeder and foundation seed production, support precision field operations, and ensure timely and quality fieldwork for key crops. Strengthening efforts include procurement of improved farm machinery, upgrading seed-research laboratories, establishing better seed processing and storage facilities, and improving mechanized field operations. This will enable higher productivity, improved seed quality, reduced labor dependency, and more efficient, research-driven farm management at the station
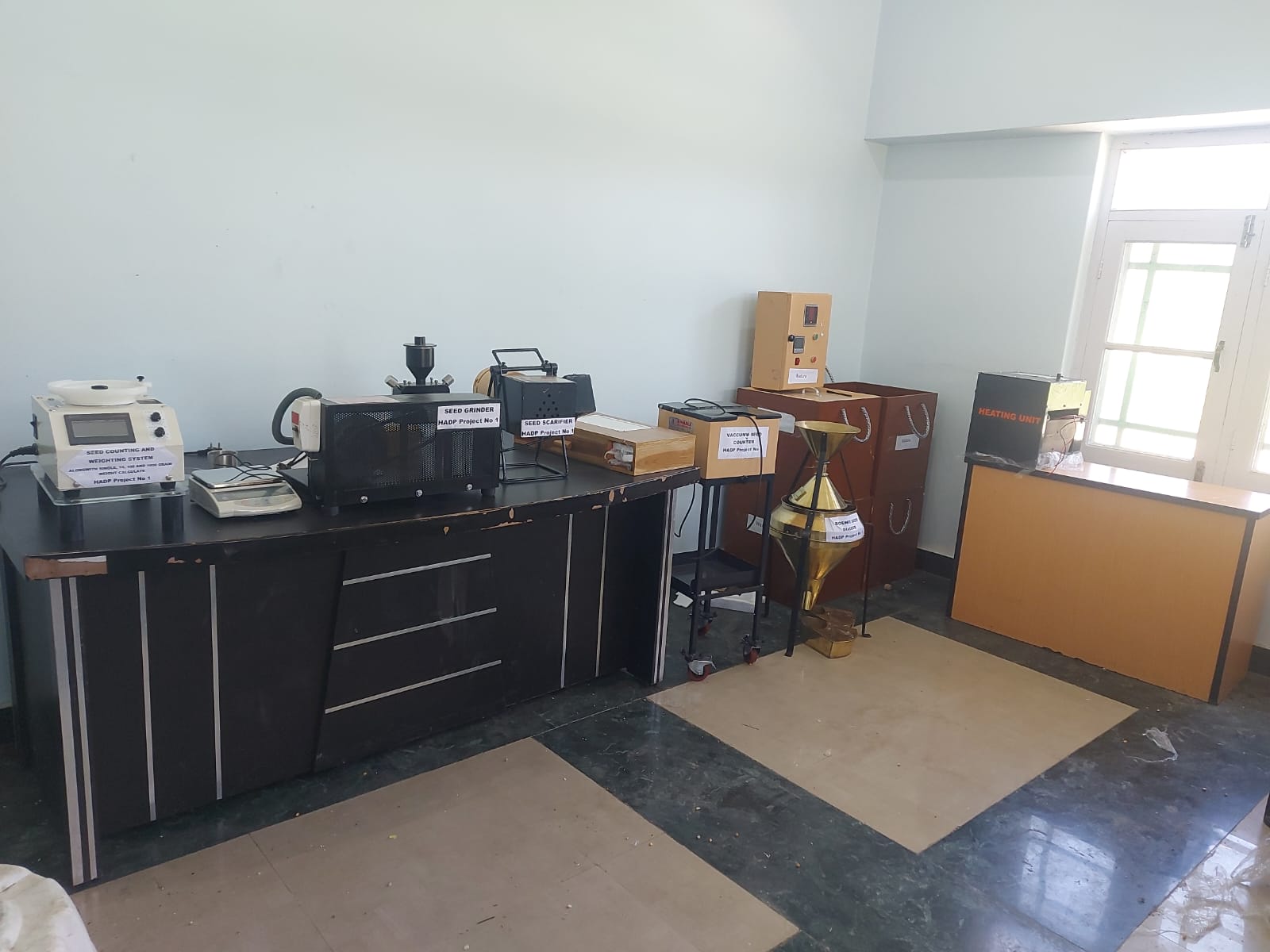

Establishment of Seed Testing Lab
To assess seed quality through scientific analysis of purity, germination, moisture, vigour, and health. It provides reliable testing services to ensure high-quality seed production, support certification processes, and strengthen overall seed quality assurance in the region
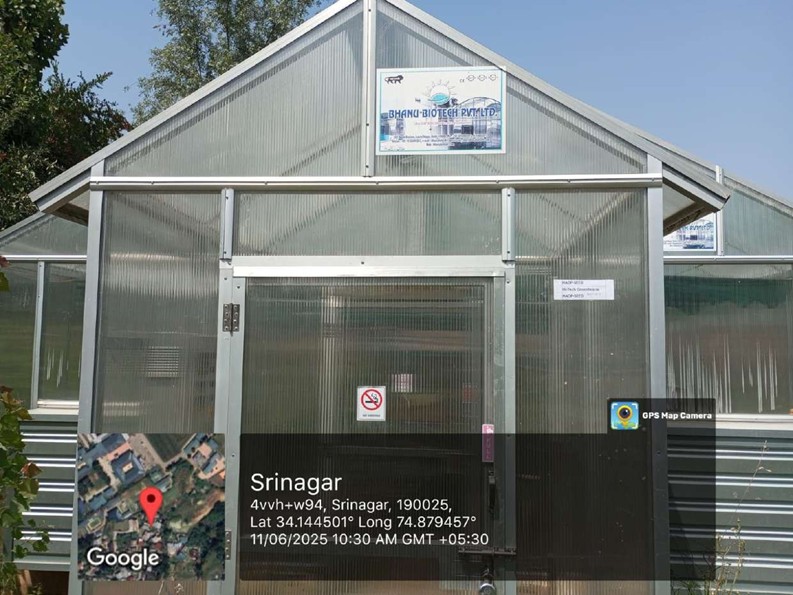

Hi Tech Greenhouse Facility
Provides a controlled environment for year-round plant cultivation.
Regulates temperature, humidity, light, and ventilation for optimal growth.
Supports research in crop improvement and protected cultivation.
Enables high-yield and disease-free seed/plant production.
Facilitates precise experiments on plant growth and environmental responses.

SEED PROCESSING UNIT
The Seed Processing Unit at MRCFC-Khudwani ensures efficient cleaning, grading, treating, and packaging of seeds to improve purity, quality, and timely availability of certified seed for distribution.

DNA Fingerprinting Lab
A DNA Fingerprinting Laboratory in the domain of plant biotechnology is a dedicated molecular facility designed to analyze the genetic makeup of plant species, varieties, and breeding materials. It is equipped with essential instruments such as PCR systems, electrophoresis units, spectrophotometers, biosafety cabinets, and imaging platforms for generating precise molecular profiles using DNA markers. The lab supports crop improvement, seed quality assurance, and varietal identification by enabling rapid, accurate, and reproducible genetic analysis. It serves as a critical support system for plant breeding programs, germplasm conservation, and biotechnology research.

Upgradation of Horticulture Lab at FoA Wadura
Upgradation of Horticulture Lab at FoA Wadura for R & D of Chilli
Upgradation of Biofertilizer Research lab at FoA wadura
Upgradation of Biofertilizer Research lab at FoA wadura for resarch trials
Upgradation of lab at division of Agronomy, FoA Wadura
Division of Agronomy, FoA Wadura lab was upgraded to carry out R & D activities of Niche Crops

Process and handling unit of chilli KVK Budgam
Establishment of Process and handling unit of chilli at KVK Budgam is under process
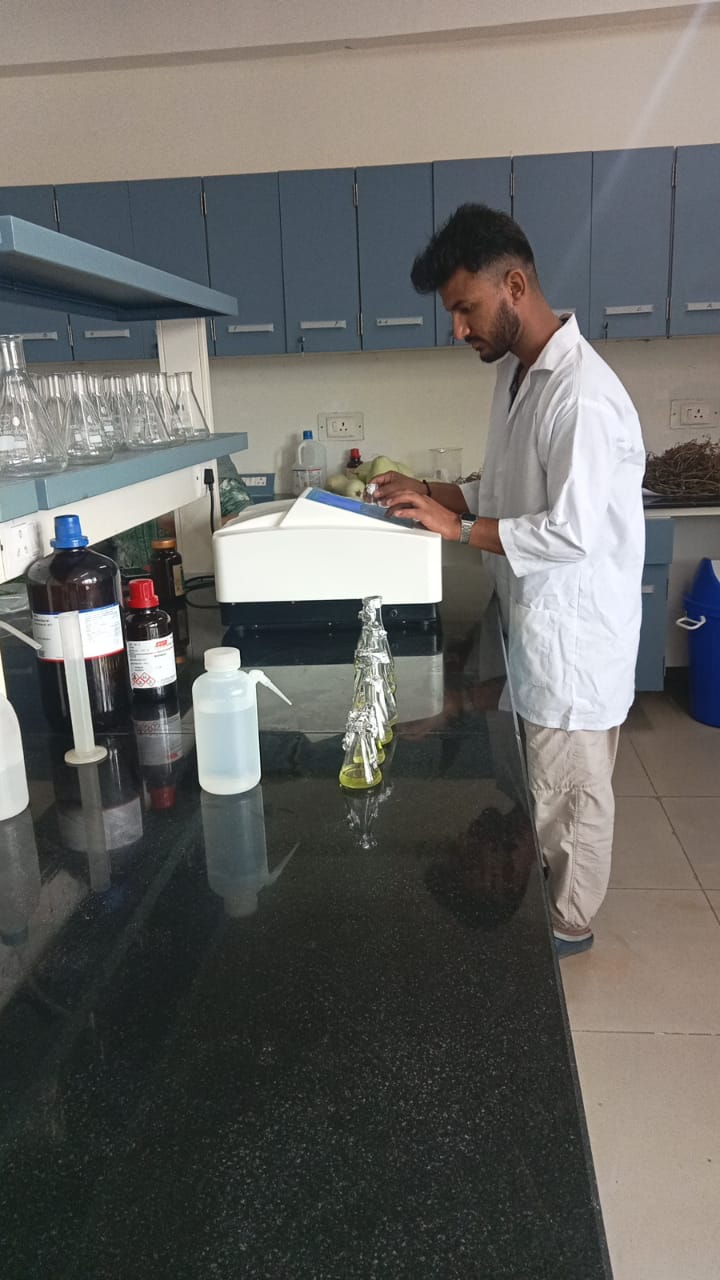

Lab facility at division of vegetable science, FoH SKUAST-Kashmir
Lab facility at division of vegetable science, was upgraded for R & D activities of niche crop (Kashmiri chili)

Process and handling unit of Red Rice at KVK Kulgam
Process and handling unit of Red Rice equiped with modern rice mill and automatic weighing and filling machine was established at KVK Kulgam
.jpeg)
Process and handling unit of Mushkbudjhi at MRCFC Khudwani
Process and handling unit of Mushkbudjhi was established at MRCFC Khudwani, equiped with modern Rice mill and automatic weighing and filling machine

Upgradation ofSoil Science Lab and GPB Quality Lab at MRCFC Khudwani
Soil Science Lab and GPB Quality Lab at MRCFC Khudwani was upgraded to carry out R & D activities of Mushkbudjhi and red rice

Upgradation of Molecular Lab facility at ARSS & TSS Dussu pampore
Molecular Lab facility was upgraded to carry out R & D activities of Niche crops

Development of Natural Farming ? Organic Farming Block at FoA Wadura
The Natural Farming / Organic Farming Block at FoA, Wadura was developed to serve as a dedicated research platform for conducting systematic studies on natural farming practices in vegetable crops. The block was established to evaluate, standardize, and validate natural and organic production technologies under local agro-climatic conditions.
Upgradation of Potato Tissue Culture Laboratory.
The Potato Tissue Culture Laboratory was upgraded to make it fully functional for advanced research and routine multiplication work. The main purpose of this upgradation is to standardize tissue culture media and protocols for newly released and advanced potato varieties developed by SKUAST-Kashmir as well as other national and international institutes that are recommended for cultivation in Jammu & Kashmir.
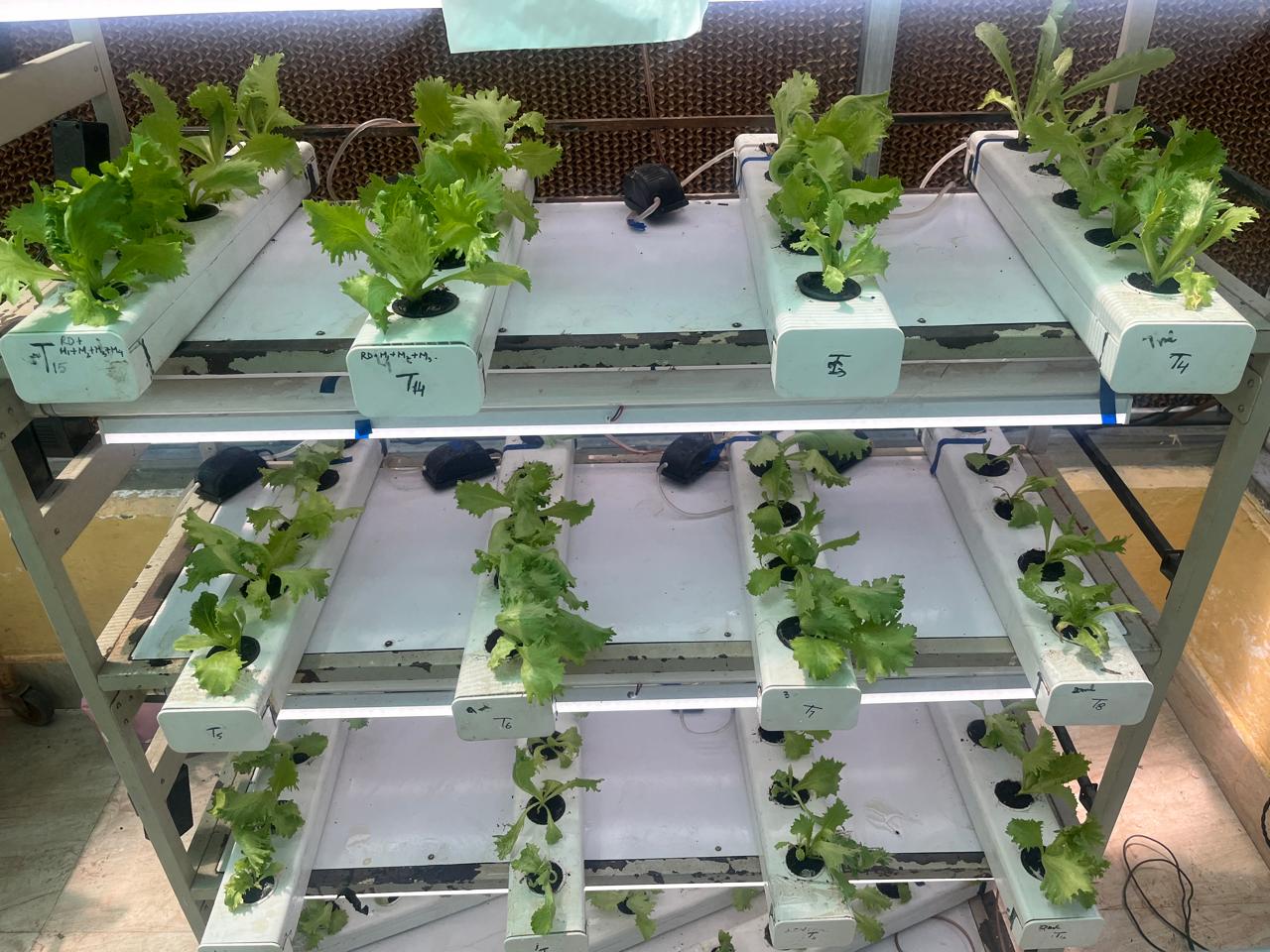

Establishment of Hi-Tech Germplasm Screening Facility
The Germplasm Screening Facility was established to systematically evaluate and screen vegetable crop germplasm under controlled environmental conditions. The primary objective of this facility is to assess biotic stresses (such as diseases etc.) and abiotic stresses (including temperature extremes, moisture stress). This targeted screening supports the development of climate-resilient vegetable varieties suited to the diverse and changing agro-climatic conditions of Jammu & Kashmir. In addition, the facility is equipped for hydroponic cultivation of vegetable crops under controlled conditions. Overall, the facility serves as a critical platform for advanced breeding, climate adaptation research, and protected cultivation technologies in the region.
Agriculture Branding Center
The Agriculture Branding Center (ABC) under HADP-04 serves as a central institutional platform for developing, standardizing, and promoting the brand identity of Jammu & Kashmir’s agricultural and horticultural products. It acts as a dedicated hub for value-chain communication, packaging innovation, GI-based product promotion, quality assurance, storytelling, and market-led brand development. The Center supports FPOs, SHGs, agri-startups, and rural enterprises by offering branding toolkits, packaging design support, digital marketing assistance, and market intelligence inputs. By integrating scientific branding practices with the region’s unique agro-biodiversity and cultural identity, the ABC aims to enhance product visibility, market access, price realization, and consumer trust across domestic and international markets.
Market Intelligence Cell
The Market Intelligence Cell (MIC) is an institutional mechanism established under HADP-04 to generate real-time, data-driven decision support for the horticulture and agriculture sectors of Jammu & Kashmir. The Cell collects, validates, and analyses daily market arrivals, prices, and trade patterns from local mandis and national terminal markets (Azadpur, Mumbai, Bangalore, etc.), integrating them with weather data, supply–demand trends, and seasonal patterns.
MIC uses AI/ML & Deep Learning based forecasting systems, digital dashboards, and analytical tools to provide accurate price forecasts, market advisories, trading window insights, and commodity intelligence for farmers, FPOs, traders, policymakers, and planners. The cell also supports enterprise development under the HADP ecosystem by providing brand analytics, competitive intelligence, and market-entry support for new agribusiness ventures.

Centre of Excellence on Herbal Technology
The Centre of Excellence on Herbal Technology is a state-of-the-art research facility established at Faculty of Forestry, SKUAST-Kashmir to advance scientific innovation in medicinal and aromatic plants. The Centre focuses on comprehensive herbal research from plant collection to authentication, and phytochemical analysis to advanced metabolite profiling, compound isolation, and biological activity evaluation. Equipped with high-end instruments viz LC-MS/MS (Triple Quad), Flash /Prep pure Chromatography system, Universal Extractor, Spectroscopic instruments, Spray Dryer, Freeze dryer etc.

MAP Germplasm bank at Faculty of Forestry, SKUAST-K
• Collection conservation and systematic evaluation of diverse accessions of priority medicinal plants from different regions of J&K.
Disease Diagnostic & Quarantine centre
Establishment of Disease Diagnostic & Quarantine Centre:
Honey bee pests and diseases will be accurately identified using a combination of methods, including visual inspection, microscopic examination, and molecular diagnostic techniques. This centre will support early detection, effective management, and prevention of disease spread in bee colonies

Bee breeding Centre for climate smart bees
Sensor-based Open Top Chamber (OTC) for Production of Climate-Smart Bees:
Bee colonies will be systematically screened for desirable traits such as high honey yield, disease tolerance, cold tolerance, and other heritable characteristics. Colonies exhibiting superior performance will be selected, and queen multiplication will be carried out from these elite colonies to develop resilient, climate-smart bee lines.

Mechanization of COTS Mirgund

Mechanization of SRS Konibal
The Saffron Research Station (SRS), Konibal has been strengthened through focused mechanization interventions, with special emphasis on the introduction of micro-irrigation systems to support sustainable saffron cultivation and precision research activities. Considering the water-scarce conditions and critical irrigation requirements of saffron, modern micro-irrigation technologies (sprinkler/drip systems) have been provided to enhance water-use efficiency and crop uniformity.

Mecanization of SKUAST-K Shalimar Farm
The mechanization initiative focuses on land preparation, sowing/transplanting, plant protection, intercultural operations, harvesting, and post-harvest handling

Mecanization of MRCS&G Shuhama
The mechanization initiative focuses on land preparation, sowing/transplanting, plant protection, intercultural operations, harvesting, and post-harvest handling

Mecanization of MRCFC Khudwani
The mechanization initiative focuses on land preparation, sowing/transplanting, plant protection, intercultural operations, harvesting, and post-harvest handling

Mechanization of MLRI Manasbal
The mechanization initiative focuses on land preparation, sowing/transplanting, plant protection, intercultural operations, harvesting, and post-harvest handling

Mechanization of Ambri Research Station, Shopian
The mechanization initiative focuses on land preparation, sowing/transplanting, plant protection, intercultural operations, harvesting, and post-harvest handling

Mechanization of FoF Benhama
The mechanization initiative focuses on land preparation, sowing/transplanting, plant protection, intercultural operations, harvesting, and post-harvest handling

Mechanization of DARS BUDGAM
(DARS), Budgam has significantly enhanced its farm operations through systematic mechanization to support research, seed production, and farmer-oriented demonstrations. The introduction of modern agricultural machinery has strengthened the station’s capacity to conduct precise field experiments, improve operational efficiency, and reduce reliance on manual labo
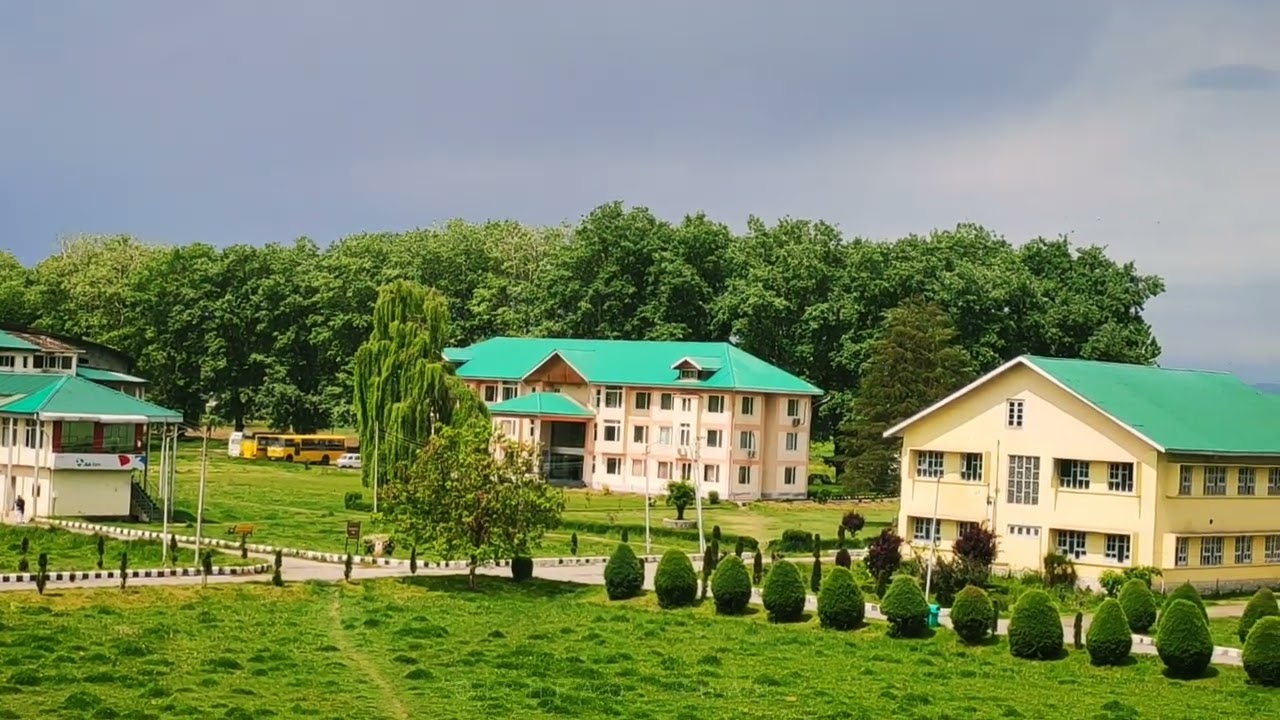

Mechanization of FOA Wadura
The Faculty of Agriculture (FOA), Wadura has taken significant steps toward strengthening farm mechanization to enhance teaching, research, and extension activities. The mechanization initiative aims to improve the efficiency of field operations, reduce labor dependency, and ensure timely agricultural practices across the instructional and research farms. A range of modern equipment—including tractors, power tillers, seeders, transplanters, sprayers, threshers have been introduced to support crop production activities from land preparation to harvesting.

Establishment of CHC at KVK Shopian
The establishment of a Custom Hiring Centre (CHC) at Krishi Vigyan Kendra (KVK) Shopian aims to strengthen farm mechanization and support the predominantly horticulture-based farming community of the district. Given the high cost of machinery and limited ownership among small and marginal farmers, the CHC will serve as a vital facility providing modern agricultural equipment on an affordable rental basis.
.jpg)
Establishment of CHC at KVK Ganderbal
The establishment of a Custom Hiring Centre (CHC) at Krishi Vigyan Kendra (KVK) Ganderbal aims to enhance farm mechanization and improve the efficiency of agricultural operations for small and marginal farmers in the district. The CHC will serve as a centralized facility where farmers can access modern farm machinery and equipment on a rental basis at affordable rates.

Establishment of CHC at KVK Pulwama
The establishment of a Custom Hiring Centre (CHC) at Krishi Vigyan Kendra (KVK) Pulwama aims to advance farm mechanization and provide small and marginal farmers with affordable access to modern agricultural machinery. The centre will function as a dedicated facility where farmers can rent equipment required for land preparation, sowing, intercultural operations, plant protection, harvesting, and post-harvest activities.

Establishment of CHC at KVK Budgam
The establishment of a Custom Hiring Centre (CHC) at Krishi Vigyan Kendra (KVK) Budgam aims to enhance the mechanization level of agriculture in the district and support small and marginal farmers who cannot afford to purchase costly machinery. The CHC will serve as a dedicated facility providing a wide range of modern agricultural equipment on a rental basis, thereby ensuring timely and efficient execution of farm operations.
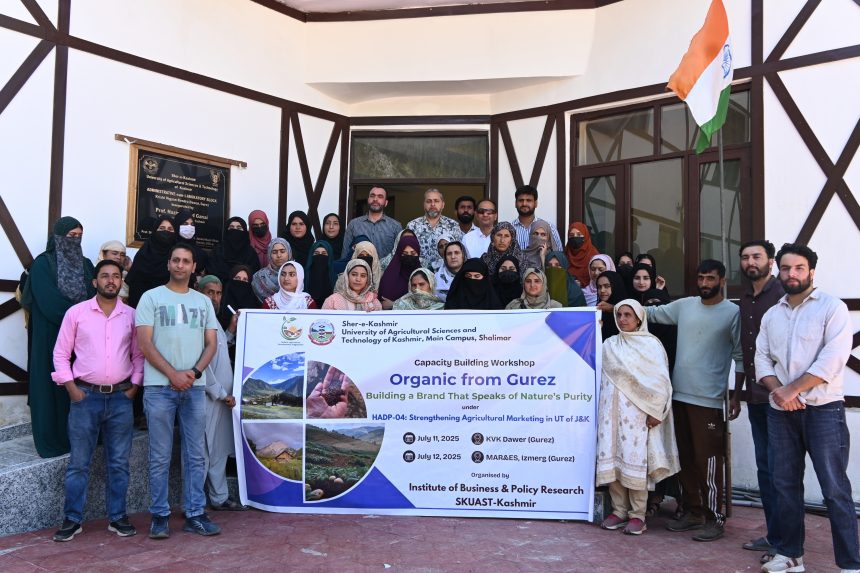

Establishment of CHC at KVK Gurez
The establishment of a Custom Hiring Centre (CHC) at Krishi Vigyan Kendra (KVK) Gurez is envisioned to significantly enhance farm mechanization in this remote and hilly region. Owing to its difficult terrain, short growing season, and limited availability of labour, farmers in Gurez face challenges in carrying out timely and efficient agricultural operations. The CHC will address these constraints by providing modern farm machinery and tools on a rental basis at affordable rates.

Establishment of CHC at KVK Kupwara
The establishment of a Custom Hiring Centre (CHC) at Krishi Vigyan Kendra (KVK) Kupwara aims to strengthen farm mechanization and provide small and marginal farmers with timely access to modern agricultural machinery on a rental basis. Given the district’s diverse terrain and labour constraints, the CHC will play a crucial role in enabling efficient and cost-effective agricultural operations.

Establishment of CHC at KVK Bandipora
The establishment of a Custom Hiring Centre (CHC) at Krishi Vigyan Kendra (KVK) Bandipora is aimed at improving the level of farm mechanization in the district by providing farmers—particularly small and marginal ones—access to modern agricultural machinery on an affordable rental basis. The initiative seeks to address issues such as high cost of machinery ownership, limited availability of equipment, and the need for timely operations during peak agricultural seasons.

Establishment of CHC at KVK Kulgam
The establishment of a Custom Hiring Centre (CHC) at Krishi Vigyan Kendra (KVK) Kulgam aims to promote farm mechanization and provide small and marginal farmers with easy access to modern agricultural machinery on a rental basis. This initiative is designed to overcome key challenges in the district, including high machinery purchase costs, limited equipment availability, and delays in critical farm operations.
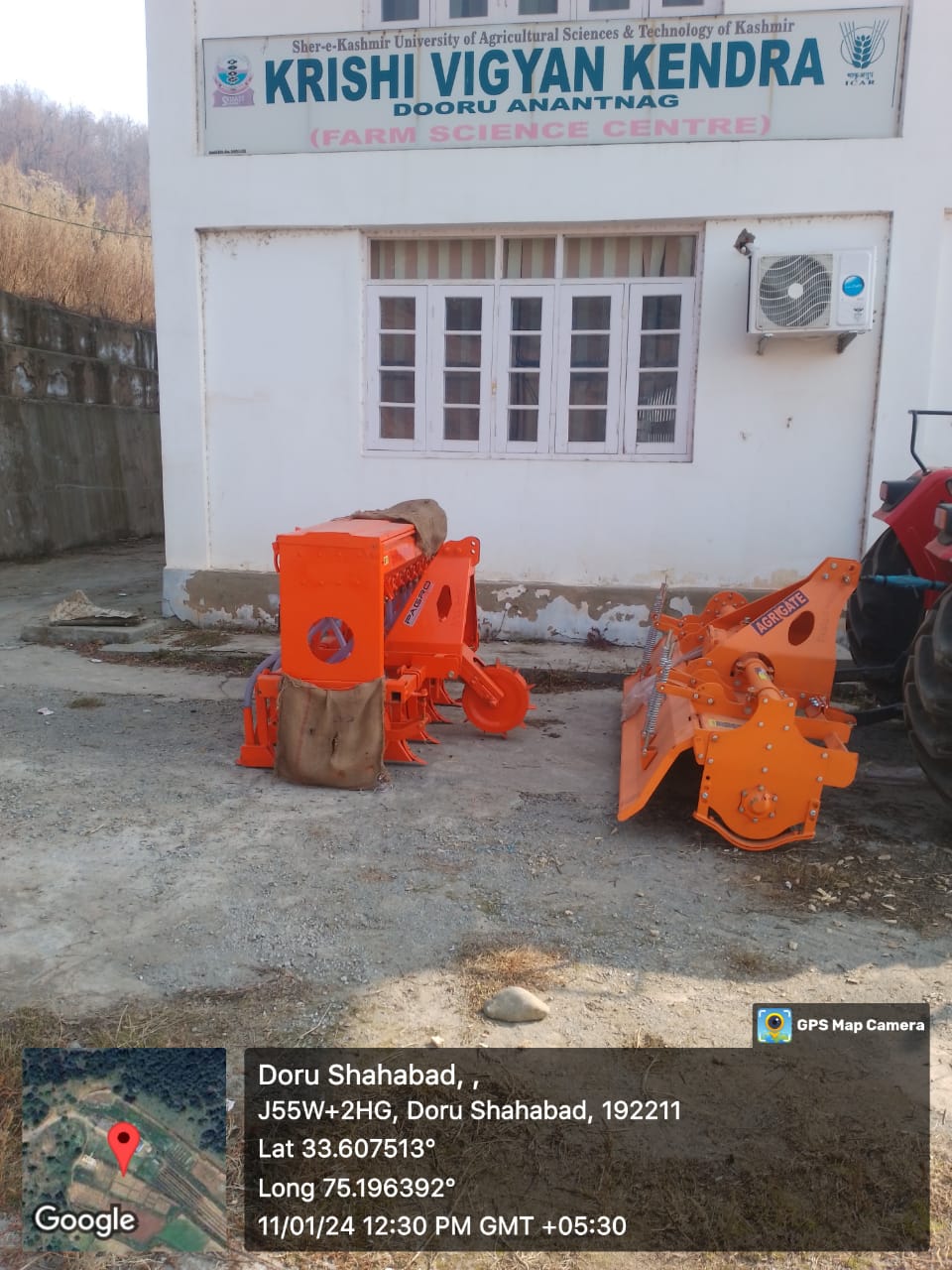

Establishment of CHC at KVK Anantnag
The establishment of a Custom Hiring Centre (CHC) at Krishi Vigyan Kendra (KVK) Anantnag is envisioned to strengthen farm mechanization and provide farmers—especially small and marginal ones—access to modern agricultural machinery at affordable rental rates. The CHC will act as a centralized facility offering a variety of equipment required for land preparation, sowing, plant protection, harvesting, and post-harvest operations.
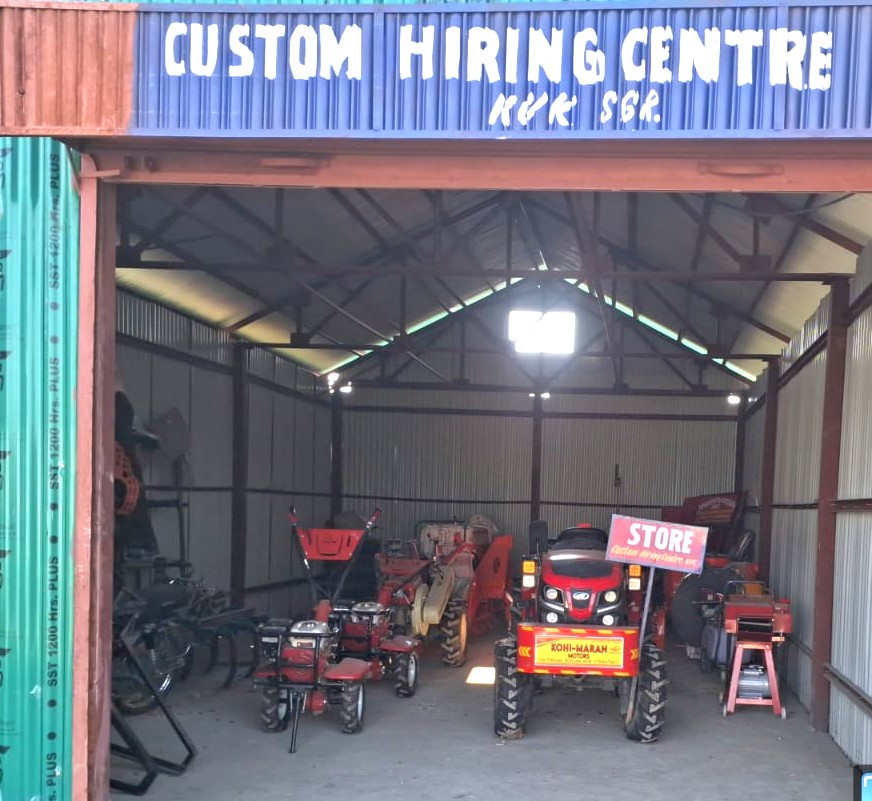

Establishment of CHC at KVK Srinagar.
The establishment of a Custom Hiring Centre (CHC) at Krishi Vigyan Kendra (KVK) Ganderbal aims to enhance farm mechanization and improve the efficiency of agricultural operations for small and marginal farmers in the district. The CHC will serve as a centralized facility where farmers can access modern farm machinery and equipment on a rental basis at affordable rates.
Custom Hiring Centre
A CHC is basically a unit comprising a set of farm machinery, implements and equipment meant for custom hiring by farmers. Though certain implements and equipment are crop specific, the traction units like tractors, power tillers etc., and self-propelled machinery like power weeder, reaper etc., are used in common. Therefore, Custom hiring centre established at Krishi Vigyan Kendras comprise farm machinery that are commonly used for tillage operations, sowing/ planting, intercultural operation, plant protection, harvesting, threshing, chaff cutting etc. The machineries are provided to farmers on rent or leased rates as approved by University.
Research & Training facility for bottle and bag cultivation of saw dust mushrooms.
Kashmir's apple industry generates at the minimum 480,000 tons of pruned wood annually (3 tons/ha).
Proposed approach: Utilize lignin-rich agro-waste as substrate for cultivation of high-value mushroom.
Limited supply of Grassy agro wastes (Wheat straw) poses challenges for cultivation of cellulosic Mushrooms in Valley.
digital seed counter
Brand: Nanbei instruments
Model: SLY-C
Micro computer automatic control
Touch key
Count speed is adjustable, high accuracy, metal shell.
Count range: small and medium sample: 0.7~4mm x 0.7~12, big sample: 3~10mm x 3~12mm

Near infra red spectrophotometer(NIR) Transmission composition analyser
Display: 5.7inches
color: LCD Touch panel
No. of channels: 8
time of measurement: 60
measurement mode: normal mode

Field laser leveler
Screw diameter(mm) 60-130
screw rotating speed(r/min) 30-50
main power(kw) 5-15
capacity(kg/h) 70-300
size 1200x2100x1200

mustard oilseed filter press
type of implement: trailed type
bucket: PB1502022LL0001
Transmitter: PAGRO PRO LASER 5000
Receiver: PAGRO LAND RECEIVER 5000
Control box: BAGRO BLADE CONTROL PANCEL 5000
Nominal width(mm) 2070
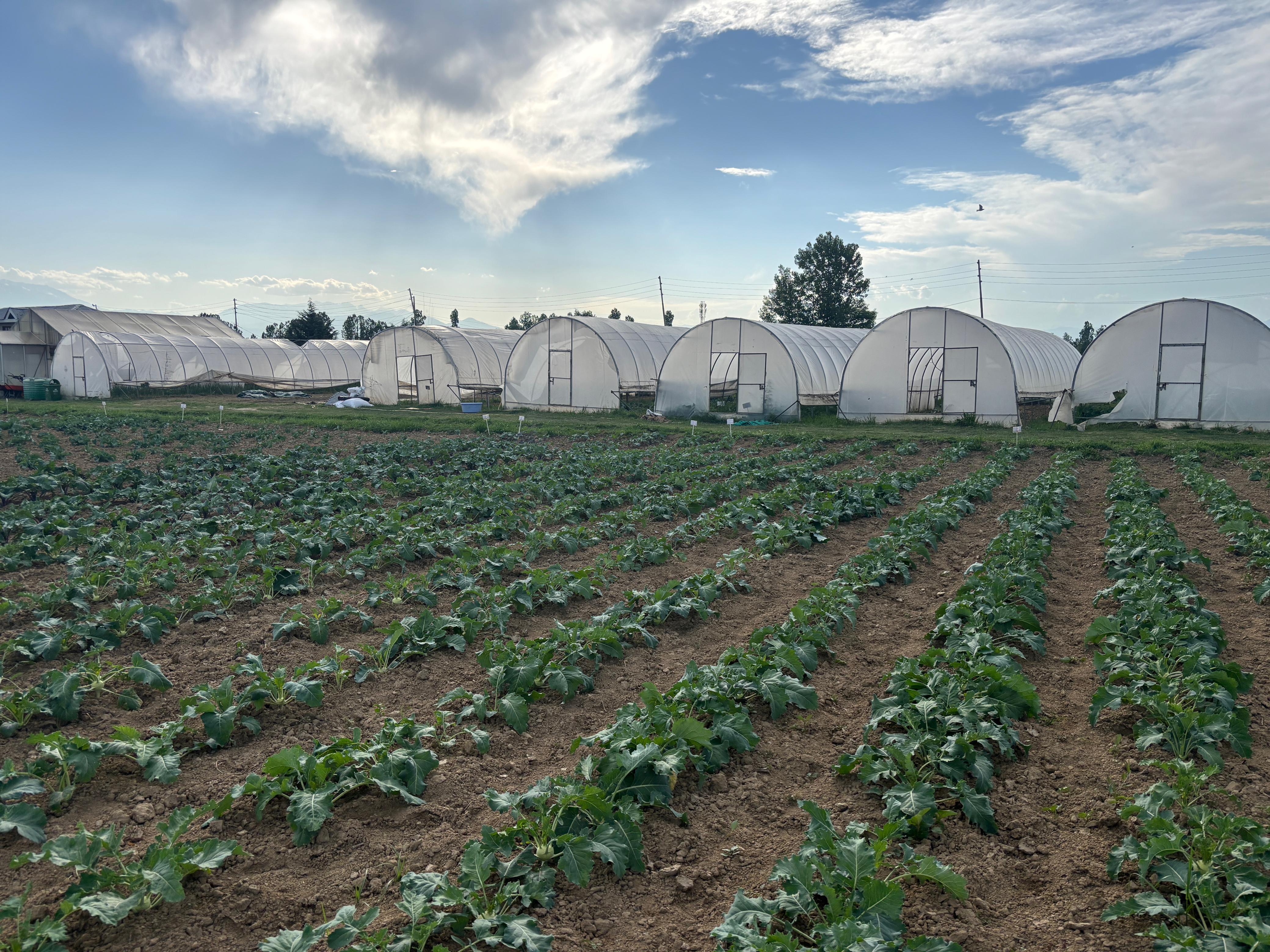

Upgradation of IFS model at Faculty of Agriculture, Wadura
Improving profitability, resource use efficiency, and sustainability for small/marginal farmers
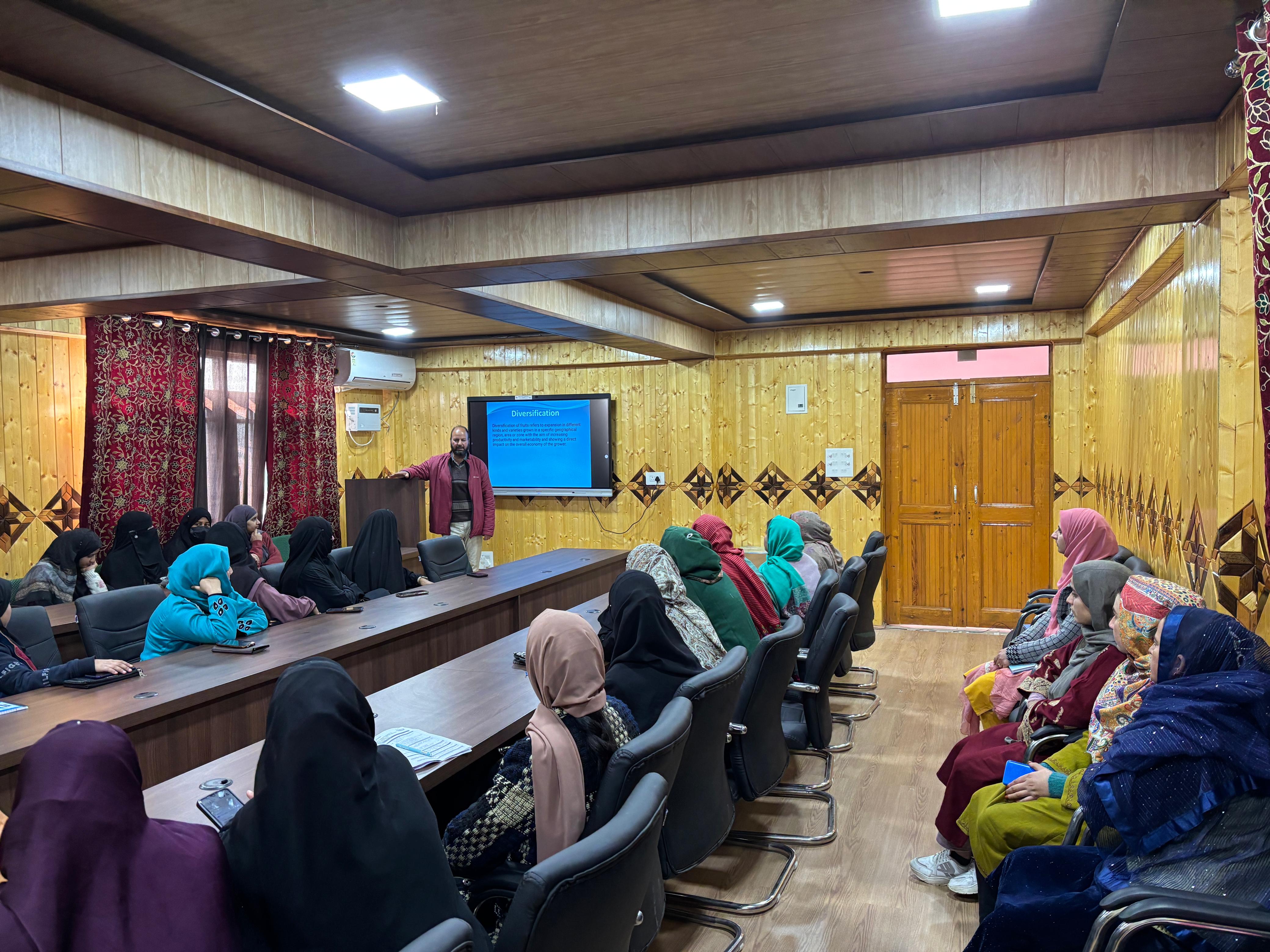

Establishment of Conference Hall at Faculty of Agriculture, Wadura, Sopore
It is established for conducting farmer trainings, meetings, demonstrations and capacity building programmes
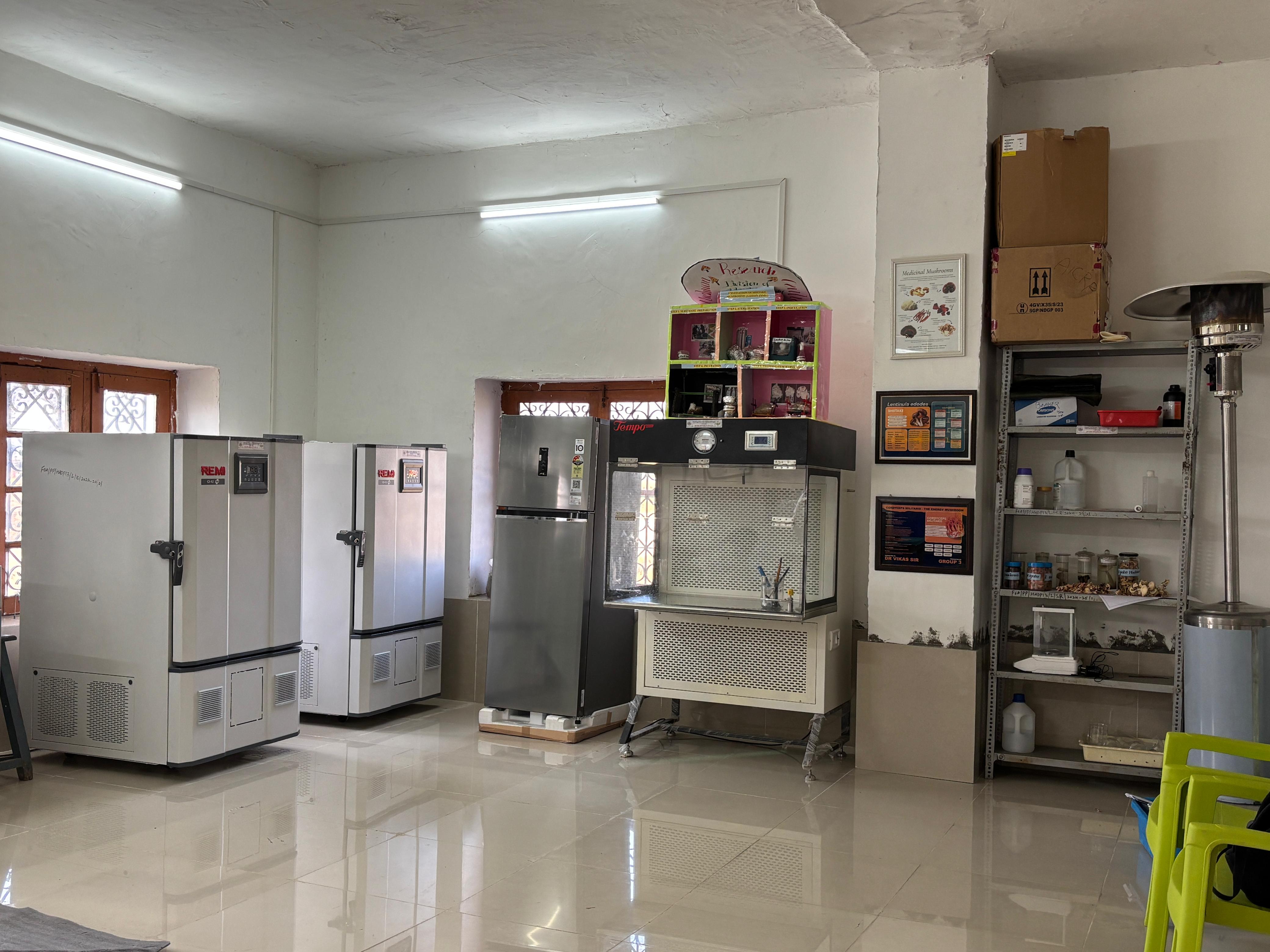

Establishment of Mushroom Unit at FoA, Wadura, Sopore
Mushroom unit is established to cultivate high-quality mushrooms. it enhances year-round production, improves resource utilization and promotes income generation for farmers.

Establishment of Livestock and Poultry unit at FoA, Wadura, Sopore
Livestock and Poultry unit is established to promote integrated animal husbandry practices and enhance farm productivity

Establishment of Apairy Unit at FoA, Wadura, Sopore
An Apairy unit has been established for scientific bee-keeping and improve honey production. It includes bee colonies, honey processing plant, bee-hives and other equipments.

Upgradation of Tissue Culture Lab
The tissue culture laboratory was upgraded to enhance its capacity for large-scale, disease-free plant propagation and advanced in vitro research. This improvement enabled standardisation of micropropagation protocols, supports research on elite ornamental and horticultural crops, and facilitates the production of quality planting material

Hi Tech Nursery
An advanced plant production system equipped with controlled-environment structures such as polyhouses, mist chambers, hardening units, and automated irrigation and fertigation. It enables year-round propagation of high-quality, disease-free planting material with uniform growth.

Model Floriculture Farm
The Model Floriculture Farm is a fully integrated facility supporting advanced research, training, and semi-commercial floriculture operations. It comprises a Walk-in Growth Chamber for controlled-environment studies, a Walk-in Cold Store for post-harvest preservation, and mechanized units such as the Eco Matpot Machine and Media Mixer for efficient nursery production. A Value Addition Laboratory enhances processing and product development capabilities. Together, these units provide a modern platform for high-quality propagation, research, and value-chain development.
.jpeg)
IFS Unit

High Tech Polyhouses

Crop Care Laboratories
3 crop care labs have been established for development of Climate resilient Agriculture

Biopesticide Production Facility
•Facility has been established at MRCFC Khudwani.
• Biopesticides ( Trichoderma based) Screening and large Scale Production (1000 liter/ Annum)

Bio- Analysis Facility
Facility has been established on pilot basis for commercial analysis of 5000-8000 samples/year for assessment of major and micronutrients, growth assessment, and sample processing to evaluate soil, plant, water, and bio-input quality.

Biofertilizer Factory
•Established at Faculty of Agriculture Wadura • Screening and Production of biofertilizers/solubilizers/conditioners
• Capacity of 40,000 liters of per annum or 400 MT of solid biofertilizers annually
AI/ML Lab
Provides advanced facilities for developing and training artificial intelligence and machine learning models. It supports research, innovation, and data-driven solutions for enhancing precision agriculture and smart farming practices.

Mechanisation of model orchards (Mist sprays, Tractors, Unmanned ground sprayers,,mounted sprayer)
The advanced machinery will ensures efficient coverage with reduced spray volume, thereby minimizing chemical use, spray drift, and wastage.
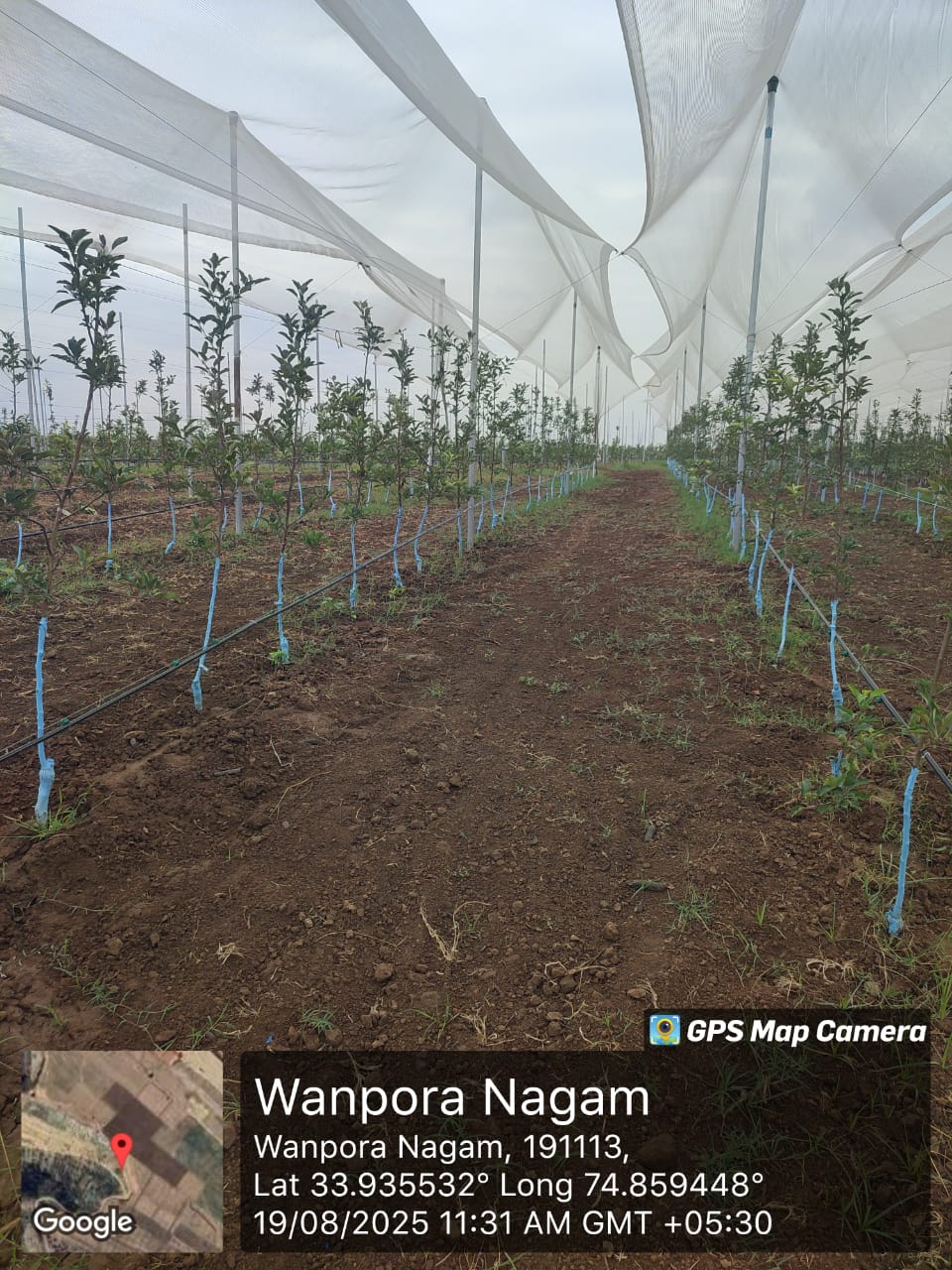

Establishment of model cluster orchards
Establishment of model cluster orchard for automation and operation inorder to showcase the reduction of 80 % in pesticide use in single cluster model orchard with an area not greater than 100 kanal and not less than 70 kanals.

development & upgradation of mycology lab and biocontrol lab with well equipped equipment's.
The development and upgradation of the Mycology and Biocontrol Laboratory is proposed to strengthen research, production, and quality control activities under the programme Minimisation of Pesticide Use in Agriculture (HADP-18). The upgradation aims to establish a well-equipped, modern laboratory facility for isolation, identification, mass multiplication, formulation, and standardization of biocontrol agents.
Advanced Analytical Chemistry Laboratory
Advanced Analytical Chemistry Laboratory providing advanced chemical analysis of soil, plant, and environmental samples for research and diagnostics.
Elemental Isotopes Laboratory
he Elemental Isotopes Laboratory carries out isotopic analysis to study nutrient dynamics, soil–plant interactions and environmental processes.
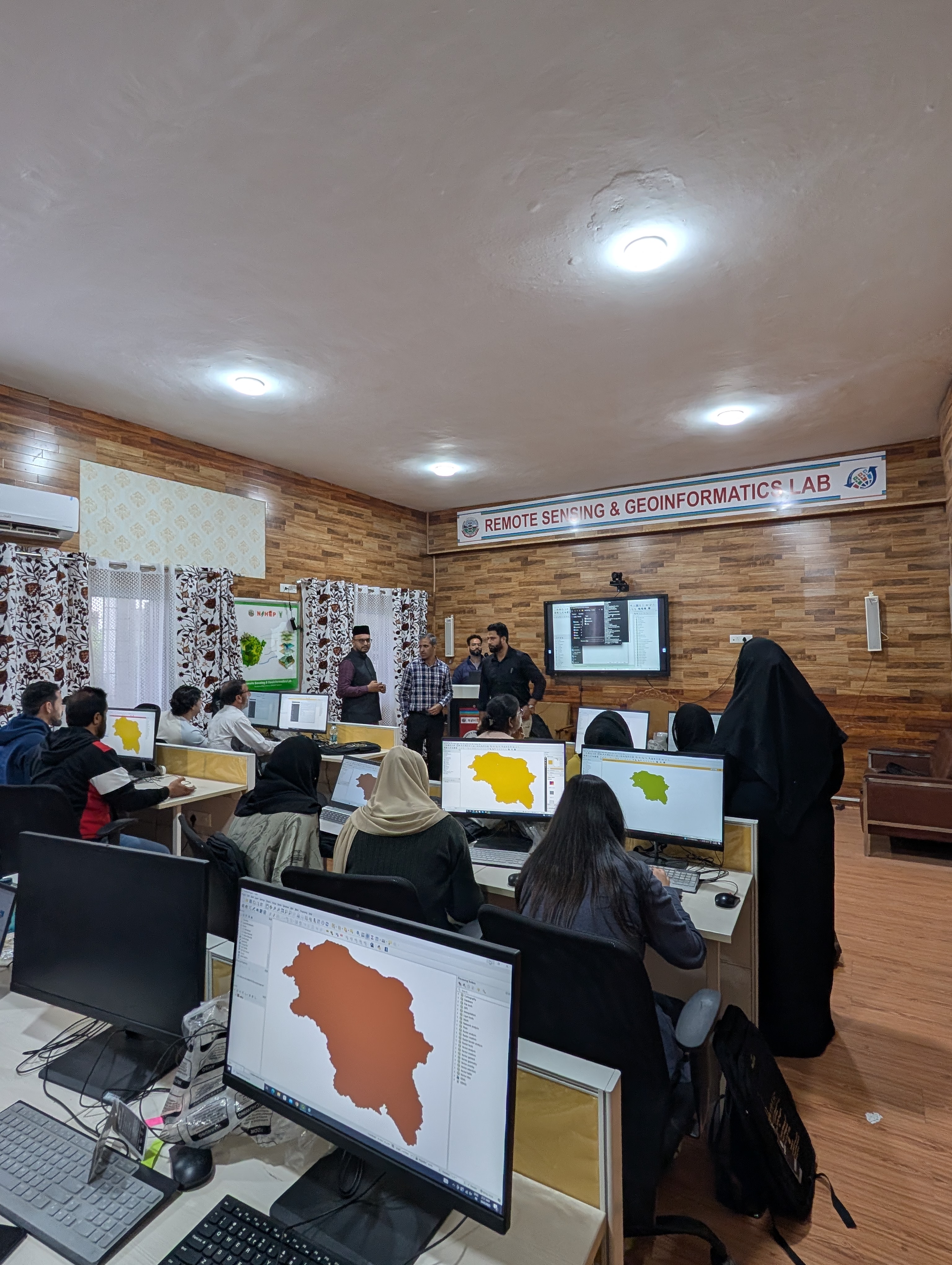

Remote Sensing (RS) & GIS Laboratory
The RS & GIS Laboratory provides facilities for spatial data analysis, land resource mapping, and decision support using satellite imagery and geospatial tools. The laboratory supports SKUAST-K researchers, students, and faculty in agricultural planning, soil and land resource assessment, watershed management, and environmental studies through advanced geospatial techniques.
Farm Land Development & Protection
Farm Land Development & Protection involves improving soil health, irrigation, and field layout while safeguarding land from erosion, flooding, and degradation. These measures enhance land productivity, ensure sustainable use, and secure long-term farm livelihoods.
Farm Land Development & Protection
Farm Land Development & Protection involves improving soil health, irrigation, and field layout while safeguarding land from erosion, flooding, and degradation. These measures enhance land productivity, ensure sustainable use, and secure long-term farm livelihoods.
Farm Land Development & Protection
Farm Land Development & Protection involves improving soil health, irrigation, and field layout while safeguarding land from erosion, flooding, and degradation. These measures enhance land productivity, ensure sustainable use, and secure long-term farm livelihoods.
Farm Land Development & Protection
Farm Land Development & Protection involves improving soil health, irrigation, and field layout while safeguarding land from erosion, flooding, and degradation. These measures enhance land productivity, ensure sustainable use, and secure long-term farm livelihoods.
Farm Land Development & Protection
Farm Land Development & Protection involves improving soil health, irrigation, and field layout while safeguarding land from erosion, flooding, and degradation. These measures enhance land productivity, ensure sustainable use, and secure long-term farm livelihoods.
Farm Land Development & Protection
Farm Land Development & Protection involves improving soil health, irrigation, and field layout while safeguarding land from erosion, flooding, and degradation. These measures enhance land productivity, ensure sustainable use, and secure long-term farm livelihoods.
Farm Land Development & Protection
Farm Land Development & Protection involves improving soil health, irrigation, and field layout while safeguarding land from erosion, flooding, and degradation. These measures enhance land productivity, ensure sustainable use, and secure long-term farm livelihoods.
Farm Land Development & Protection
Farm Land Development & Protection involves improving soil health, irrigation, and field layout while safeguarding land from erosion, flooding, and degradation. These measures enhance land productivity, ensure sustainable use, and secure long-term farm livelihoods.
Farm Land Development & Protection
Farm Land Development & Protection involves improving soil health, irrigation, and field layout while safeguarding land from erosion, flooding, and degradation. These measures enhance land productivity, ensure sustainable use, and secure long-term farm livelihoods.
Other Lab. facility
Other Laboratory Facilities include essential equipment and support services for sample preparation, analysis, storage, and safety, enabling smooth conduct of research, testing, and experimental activities.
Plant / Animal Disease Diagnosis Facility
Plant / Animal Disease Diagnosis Facility provides scientific identification of diseases through observation, laboratory testing, and analysis, helping in timely treatment, prevention, and improved plant and animal health.
Soil Testing
Soil Testing is the scientific analysis of soil to determine its nutrient content, pH level, and overall fertility. It helps in selecting suitable crops, deciding the correct type and quantity of fertilizers, and improving soil health for better crop yield.
Cyber Extension Centre
Cyber Extension Centre (CEC) a centralized facility housing Computing, Networking equipments, Storage systems and infrastructure that support IT Operations. It focuses on the Operations like Manage, Process, Store, and distribute data. Its features are designed around high availability, efficiency, security, and scalability
Nodal ICT Centre
Training-cum-Meeting Hall
The Training-cum-Meeting Hall is a well-equipped, spacious facility designed to host training programmes, workshops, and official meetings in a professional environment. It is furnished with modern audio-visual aids and comfortable seating to facilitate effective learning and deliberations.
IT enabled Smart Training Facility
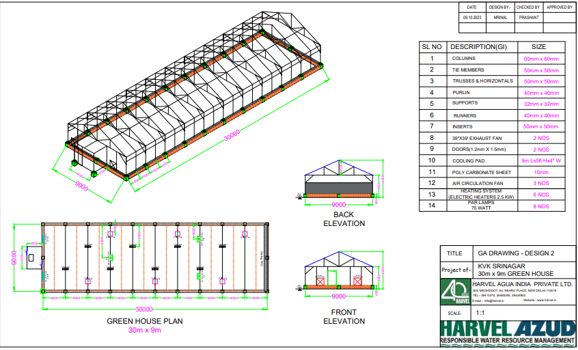
Hi-Tech Protected Cultivation Structures (Polyhouses)
Hybrid power supply (3-phase electric + Solar)
Sensors with IoT support
Fertigation system
Boomer (1/2 each polyhouse)
Rootstock Bank at SKUAST-K, Wadura
This initiative aims to conserve, multiply, and supply high-quality rootstocks. By maintaining a diverse collection of rootstocks with traits such as disease resistance, drought tolerance, and adaptability to different soil conditions, the bank ensures a reliable foundation for grafting elite scion varieties. This initiative supports orchard establishment, promotes uniformity and vigor in fruit crops, and enhances long-term productivity and sustainability in horticulture. Also, it will promote domestic production of quality planting material leading to reduced imports, genetic diversity conservation, extension services, development of breeding programmes

Rootstock Bank at SKUAST-K, Shuhama
This initiative aims to conserve, multiply, and supply high-quality rootstocks. By maintaining a diverse collection of rootstocks with traits such as disease resistance, drought tolerance, and adaptability to different soil conditions, the bank ensures a reliable foundation for grafting elite scion varieties. This initiative supports orchard establishment, promotes uniformity and vigor in fruit crops, and enhances long-term productivity and sustainability in horticulture. Also, it will promote domestic production of quality planting material leading to reduced imports, genetic diversity conservation, extension services, development of breeding programmes

Mother Orchard of Cherry at KVK, Ganderbal
This initiative focuses on the development and introduction of new plant varieties with improved traits such as higher yield, enhanced nutritional quality, resistance to pests and diseases, and adaptability to diverse climatic conditions. It will serve as a reliable source for the production of true-to-type budwood and graftwood.

Mother Orchard of Walnut at SKUAST-K, Shalimar
This initiative focuses on the development and introduction of new plant varieties with improved traits such as higher yield, enhanced nutritional quality, resistance to pests and diseases, and adaptability to diverse climatic conditions. It will serve as a reliable source for the production of true-to-type budwood and graftwood.

Mother Orchard of Apple at KVK, Pulwama
This initiative focuses on the development and introduction of new plant varieties with improved traits such as higher yield, enhanced nutritional quality, resistance to pests and diseases, and adaptability to diverse climatic conditions. It will serve as a reliable source for the production of true-to-type budwood and graftwood.
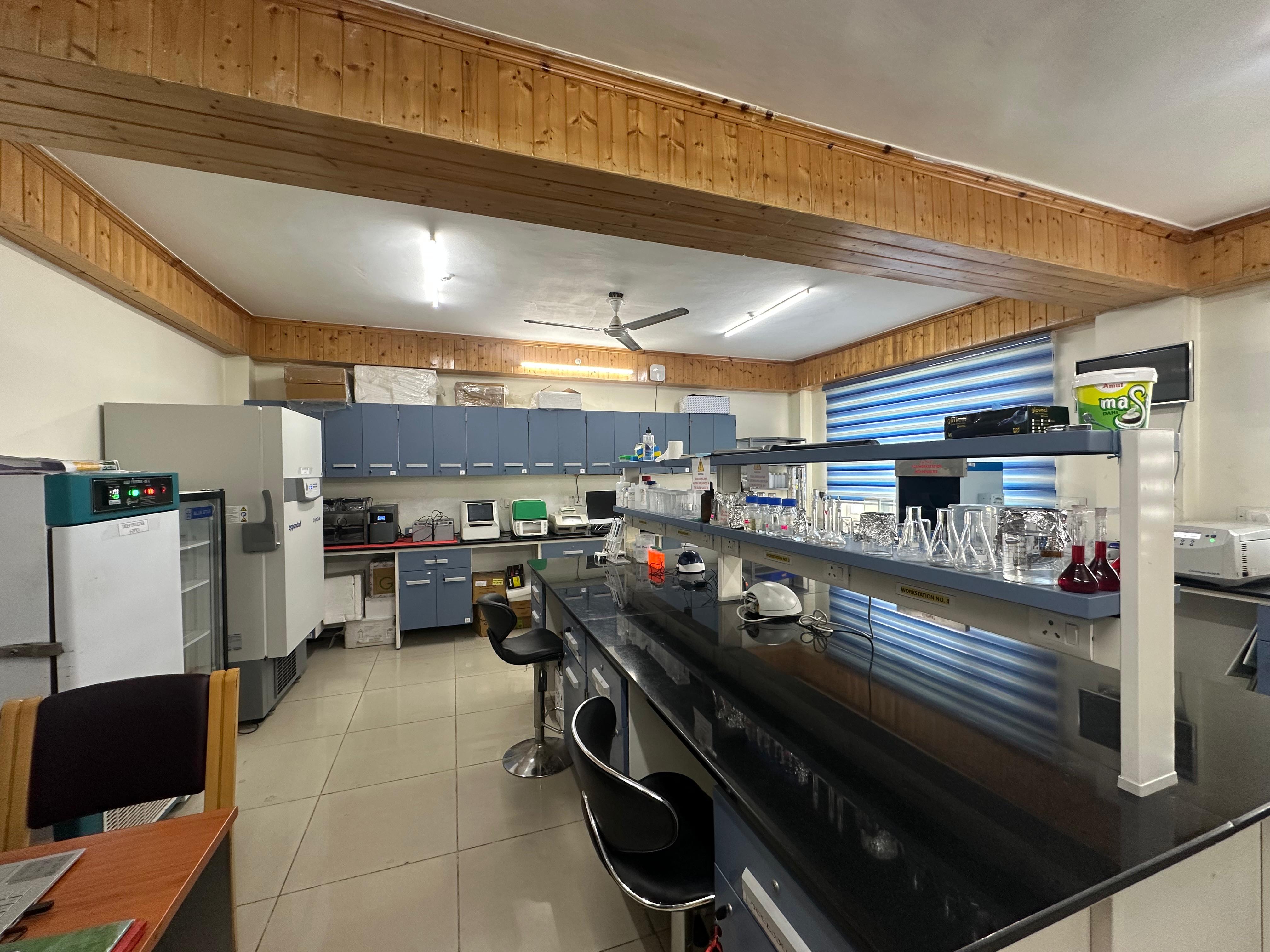

Strengthening and augmentation of plant material testing and micro propagation units/virus indexing through labs
This initiative focuses on the certification of planting material to guarantee genetic purity, true-to-type characteristics, and freedom from pests and diseases. Also, cutting-edge tissue culture laboratory to support mass propagation of high-quality, disease-free planting material for horticultural crops.
Mechanization, Automation and Upgradation of Nurseries
Mechanization, automation, and upgradation of nurseries involve the adoption of modern tools, equipment, and technologies to improve efficiency, precision, and quality in nursery operations.
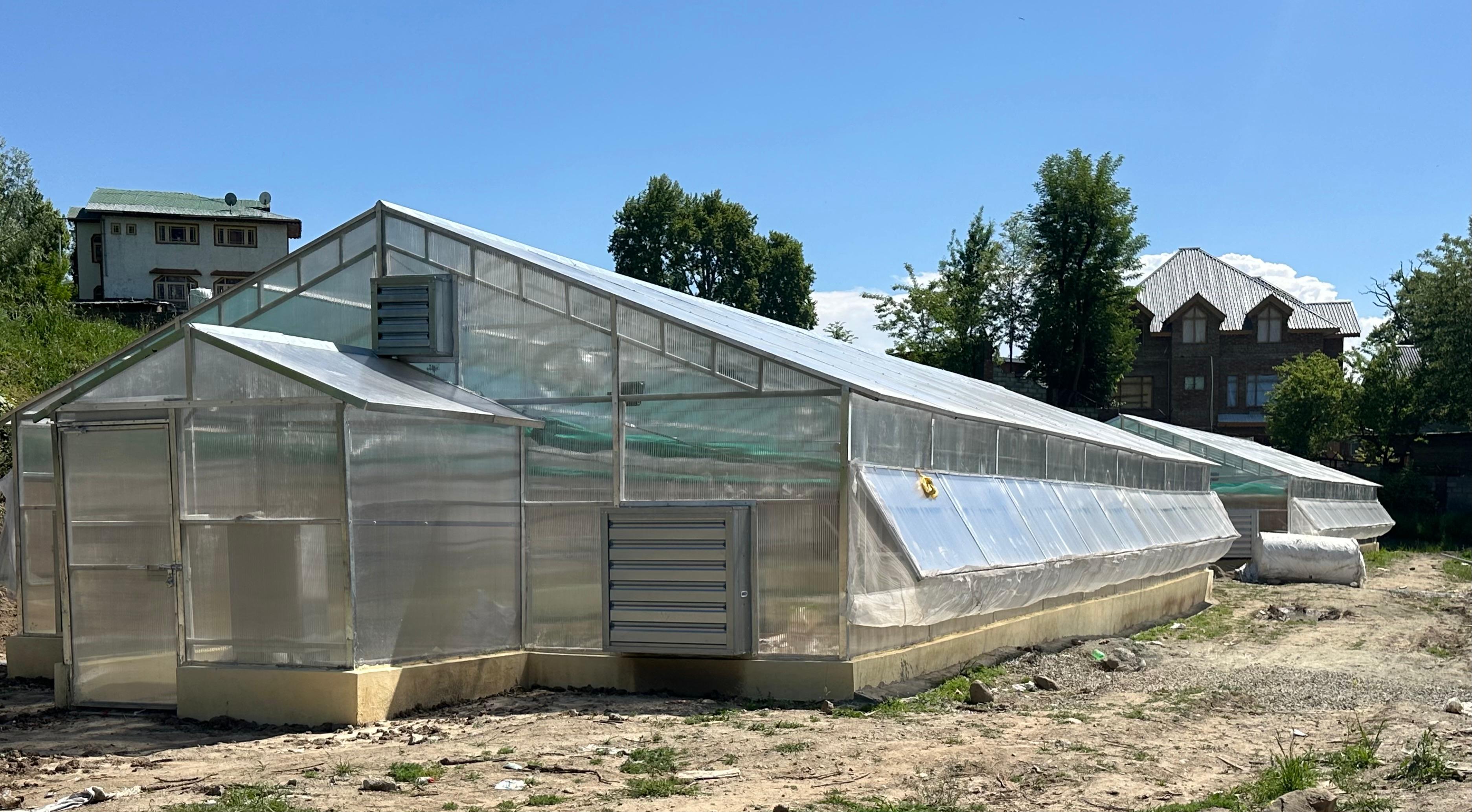

Establishment of Hi-Tech Green Houses (Protected cultivation)
Hi-tech greenhouses are advanced protected cultivation structures designed to provide a controlled growing environment for crops. These structures are equipped with modern technologies such as temperature and humidity control, automated irrigation and fertigation systems, ventilation, shading, and sometimes climate-controlled heating/cooling systems. By regulating environmental factors, hi-tech greenhouses enable year-round cultivation of high-value plants with optimal growth conditions.
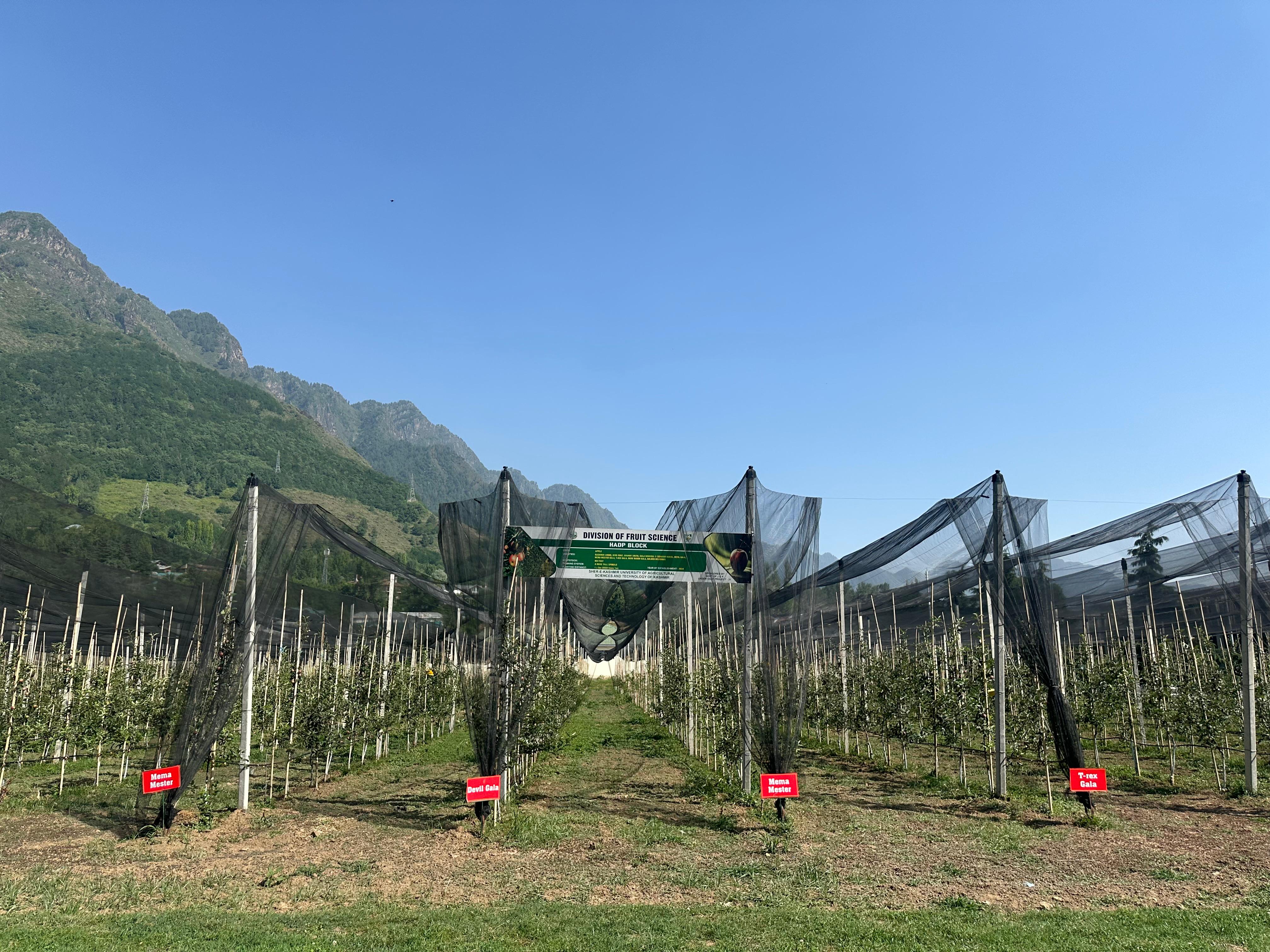

Mother Orchard of Apple at SKUAST-K, Shalimar
This initiative focuses on the development and introduction of new plant varieties with improved traits such as higher yield, enhanced nutritional quality, resistance to pests and diseases, and adaptability to diverse climatic conditions. It will serve as a reliable source for the production of true-to-type budwood and graftwood.

Rootstock Bank at SKUAST-K, Shalimar
This initiative aims to conserve, multiply, and supply high-quality rootstocks. By maintaining a diverse collection of rootstocks with traits such as disease resistance, drought tolerance, and adaptability to different soil conditions, the bank ensures a reliable foundation for grafting elite scion varieties. This initiative supports orchard establishment, promotes uniformity and vigor in fruit crops, and enhances long-term productivity and sustainability in horticulture. Also, it will promote domestic production of quality planting material leading to reduced imports, genetic diversity conservation, extension services, development of breeding programmes
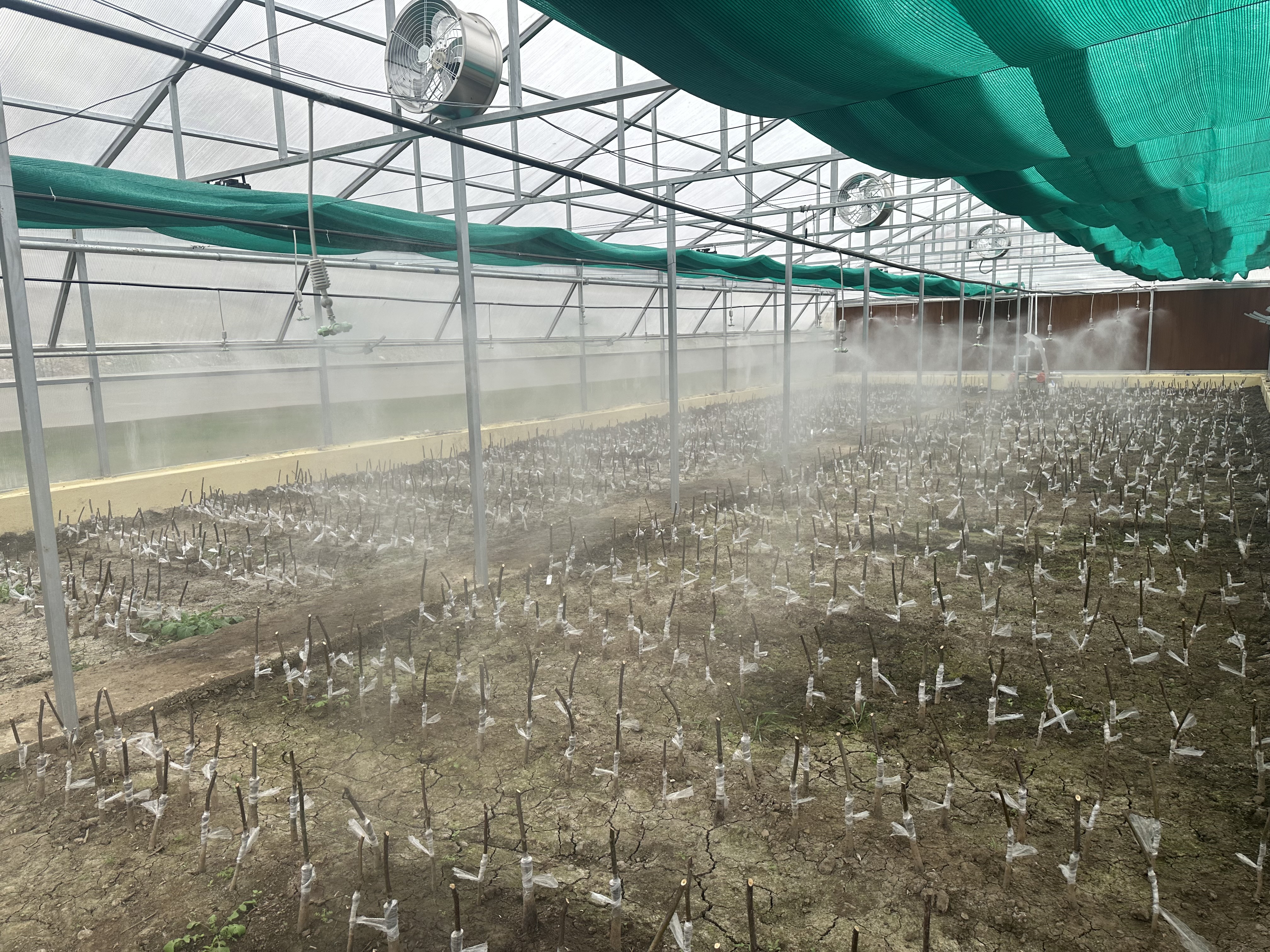

Establishment of Plant Propagation unit (Nursery)
This initiative adopts the hub and spoke model to streamline the production and distribution of certified, high-quality planting material. Centralized "hub" nurseries equipped with advanced propagation facilities focused on producing elite mother plants and rootstocks. These are then distributed to "spoke" nurseries located closer to farming communities for further multiplication and easy access. The model ensures consistency in plant quality, faster dissemination of improved varieties, and greater outreach to farmers, thereby supporting large-scale orchard establishment and improved productivity.
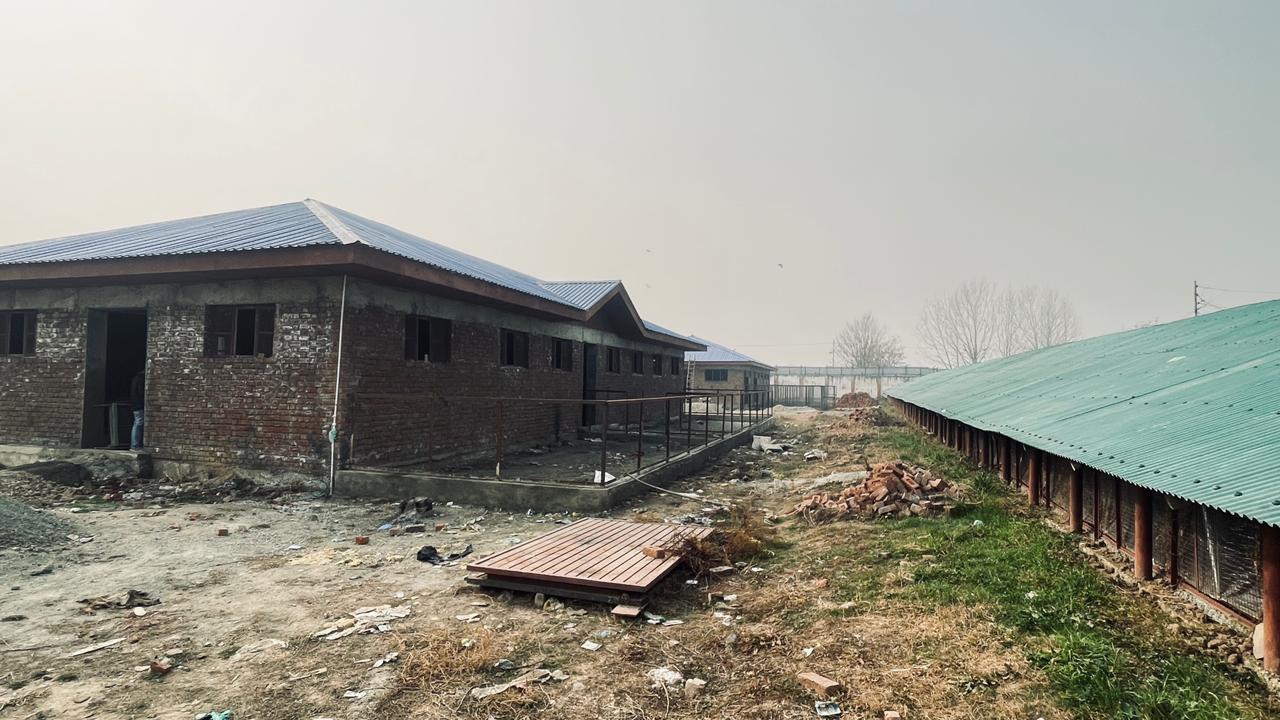

2. Establishmnet of calf rearing Station
Calf Rearing Station is a scientific housing facility for rearing of elite male calves that shall be born out of Embryo transfer, whether at Field or organised farm level.
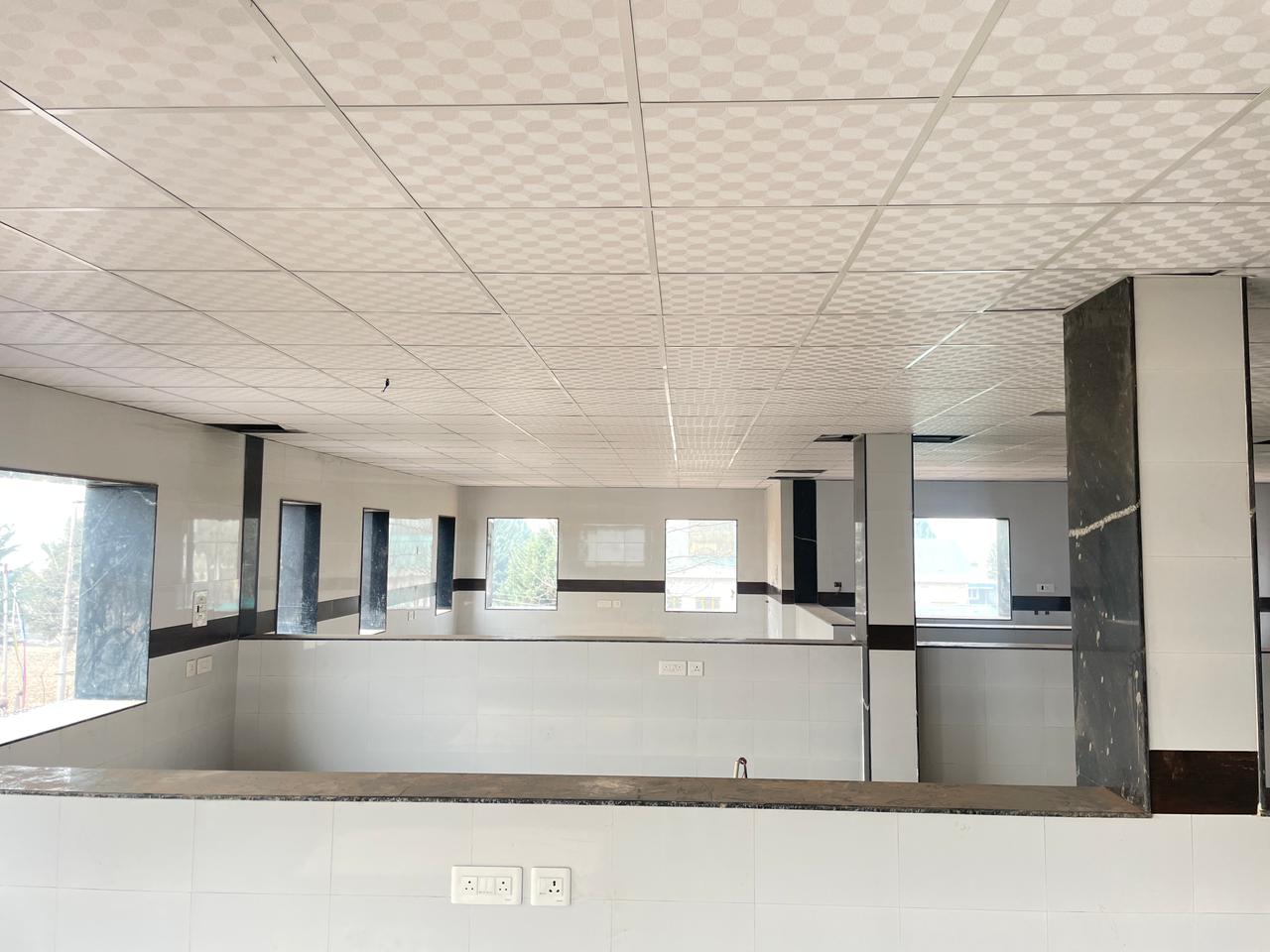

Establishment of MOET-IVF Facility
MOET-IVF Facility shall be an Assisted Reproductive Technology center which shall cater to implementation of ART in dairy animals-especially Jersey cattle for rapid multiplication and dissemination of the elite germplasm for ensuring faster genetic gain of dairy germplasm
upgradation of Labs in AGB and Vety clinical complex
Lab facilities created, standardization of techniques for evaluation studies - candidate gene approach
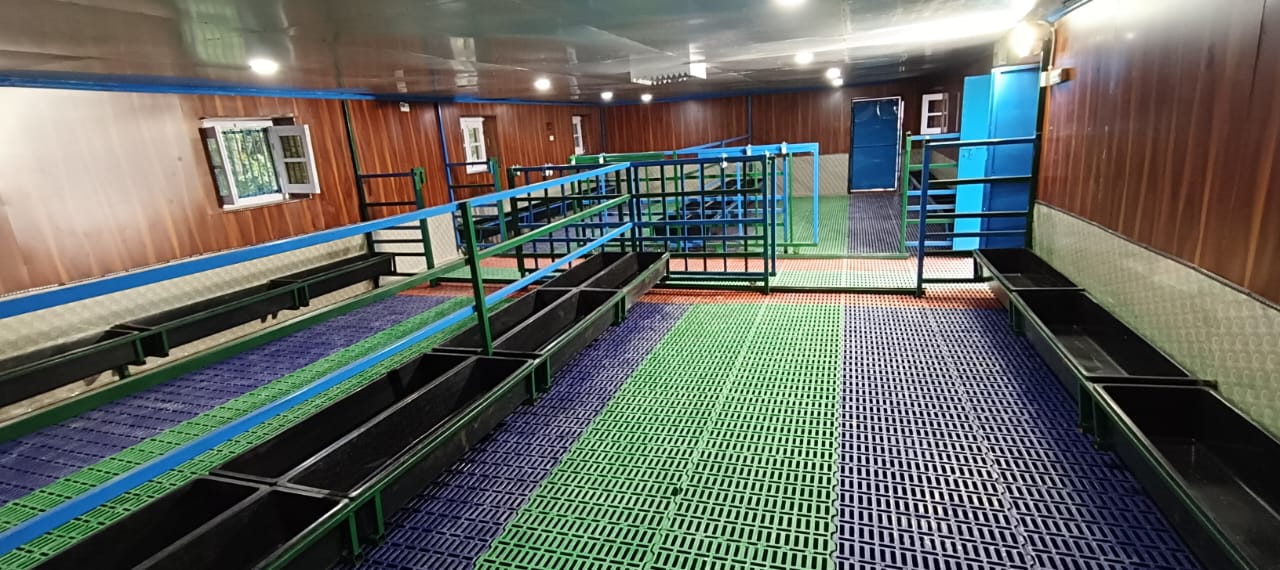

Technology /upgradation enabling of SKUAST-K Research Farm
HADP- 25 Roadmap for Poultry Development in J&K
1. Remodeling of parent stock shed.
2. Creation of breeding pens for rearing of parent stock and crossbred birds.
3. Installation of equipment necessary for vaccine development.
4. A computational facility was created for vaccine designing.
5. Installation of equipment necessary for the disease diagnosis laboratory.
6. Construction of a shed for a mini feed mill.
7. Installation of equipment for analysis of proximate principles for low-cost feed formulation.
Value addition and product development.
In Jammu and Kashmir mostly due to climatic conditions people consume a lot of animal protein in different forms, it is necessary to add value to the fishes produced so that more employment is generated and more fish products are formed and people will have enough choices for selection of these varied fish products.
Disease diagnosis & prophylaxis.
A large proportion of the population of the fishes starting from the eyed stage to brooders is lost due to certain diseases out breaks, therefore in order to control this loss, a disease diagnostic and Health management needs to be taken.
Genetic interventions for growth and breeding in cold water fishes
The Trout fish grows to table size in eighteen months and the breeding period is short mainly from November to February. This short breeding period leads to the saleable fish in one particular period while in other periods we don’t have enough saleable biomass. Likewise if the growth of the fish is reduced from eighteen months to fourteen or twelve months, the production of the fish will increase many folds.
Development of low cost feed
The ingredients of the Trout Fish feed are mostly imported from the maritime states of India and that is the reason of high cost of the feed. As a result a good amount of the earning of the farmer goes on feed cost.
The Division of Fish Nutrition and Biochemistry (FNB), Faculty of Fisheries, SKUAST-K is undertaking this research programmes for the development, demonstration and commercialization of cost effective fish feed technology from the locally available ingredients for coldwater aquaculture.
Needle punching Felting line
The university has established an advanced Needle Punching Felting Processing Line to support teaching, research, and product development in nonwoven and fibre technology. The facility comprises fibre opener, feeder, card, cross-lapper, needle punching and cutter, enabling end-to-end processing of natural and synthetic fibres into high-quality nonwoven felts.
This integrated setup allows experimentation with diverse fibre types and process parameters, facilitating innovation in geotextiles, insulation materials, craft felts, agro-felts, and industrial nonwoven products. The facility serves as a platform for students, researchers, and artisans to gain hands-on exposure to modern nonwoven manufacturing techniques while supporting prototype development, standardization, and extension activities. It also strengthens the university’s capacity for research collaboration, training programmes, and technology-driven enterprise development in the fibre and textile sector.
Fur processing unit
Sheep slaughtering, in addition to supplying mutton, generates a substantial volume of high-value by-products that often go unaccounted for in economic evaluations. Among these, sheep skins are particularly important, comprising nearly 7–11% of the animal’s live weight. Despite their significant market potential, these skins remain largely underutilized, resulting in considerable revenue losses that could otherwise support rural livelihoods and strengthen the livestock value chain.
In the Union Territory of Jammu & Kashmir, an estimated 5,000–6,000 pelts are produced each day. However, due to the absence of a dedicated processing and value-addition industry, most of these pelts are discarded, allowed to deteriorate, or sold at nominal prices. This leads to the wastage of a resource with high commercial value and limits income-generating opportunities for local communities. Systematic collection, proper grading, and scientific processing into premium fur and leather products could multiply their market value manyfold. Such value addition has the potential to revive Kashmir’s once-flourishing fur industry, renowned historically for its exceptional craftsmanship.
The establishment of a fur processing unit will not only introduce environmentally friendly and modern pelt-processing technologies but also serve as a centre for capacity building, incubation, and entrepreneurial demonstration. This facility can play a pivotal role in developing skilled human resources, fostering innovation, supporting startups, and creating sustainable livelihood opportunities in the region.
Animal Fiber Quality Assurance Laboratory
India is home to a rich diversity of livestock, including sheep, with 42 recognized breeds distributed across various agro-climatic regions, collectively producing about 45.10 million kilograms of wool annually. The Union Territory of Jammu & Kashmir contributes significantly to this sector, yielding 7.53 million kilograms of some of the finest quality wool in the country. In addition to wool, India also produces several specialty animal fibres derived from goats, rabbits, and camels—renowned for their superior fineness, lustre, warmth, softness, elegance, and aesthetic appeal. Among these, Pashmina stands out as a premium luxury fibre, celebrated both nationally and internationally.
Despite this rich resource base, the accurate assessment of raw animal fibres and their value-added products remains crucial for determining marketability and end-use potential. A persistent limitation in the fibre sector has been the lack of awareness and access to reliable quality testing facilities, which directly impacts the income, confidence, and market opportunities of stakeholders. Consequently, establishing a dedicated, credible quality assurance facility has become essential to ensure the sustainable development and global competitiveness of India’s animal fibre industry.
In this context, Sher-e-Kashmir University of Agricultural Sciences and Technology of Kashmir (SKUAST-K), as an innovation-driven farm university, has established a Centre of Excellence (CoE) on fibre testing entitled “Animal Fiber Quality Assurance Laboratory” at FVSc & AH, Shuhama. The facility has been created with the support of the Government of J&K under the HADP project “Promotion of Wool and Pelt for Effective Processing and Marketing.”
High-throughput Phenotyping & Speed-Breeding Unit
The High-Throughput Phenotyping & Speed-Breeding Unit is an advanced controlled-environment facility designed to accelerate crop improvement by enabling rapid generation advancement and precise trait measurement. The unit integrates extended photoperiods, optimized temperature and humidity regimes, and LED-based light spectra to reduce crop generation time, often achieving 3–6 generations per year depending on the crop.
High-throughput phenotyping platforms equipped with automated imaging (RGB, thermal, multispectral), sensor-based growth monitoring, and data analytics allow non-destructive, time-series assessment of key traits such as plant vigor, biomass accumulation, stress tolerance, flowering behavior, and yield components.
The facility supports genetics, breeding, and functional genomics research, enabling faster selection, early screening of large populations, and rapid integration of superior genotypes into breeding pipelines, particularly for cereals, legumes, oilseeds, and fodder crops.
Hydroponics Fodder Unit
A hydroponics unit is a soil-less cultivation system where plants or green fodder are grown using water enriched with essential nutrients under a controlled environment. Seeds (such as maize, barley, oats, sorghum, or legumes) are placed in trays or channels and supplied with nutrient solution through sprinkler, drip, or flow systems.
The unit ensures rapid biomass production, uniform growth, and high nutrient-use efficiency while requiring minimal water, land, and labour. Hydroponic fodder units typically produce fresh, palatable, and nutritious fodder within 7–10 days, making them ideal for livestock feeding, research, and climate-resilient agriculture, especially in land- and water-scarce regions.
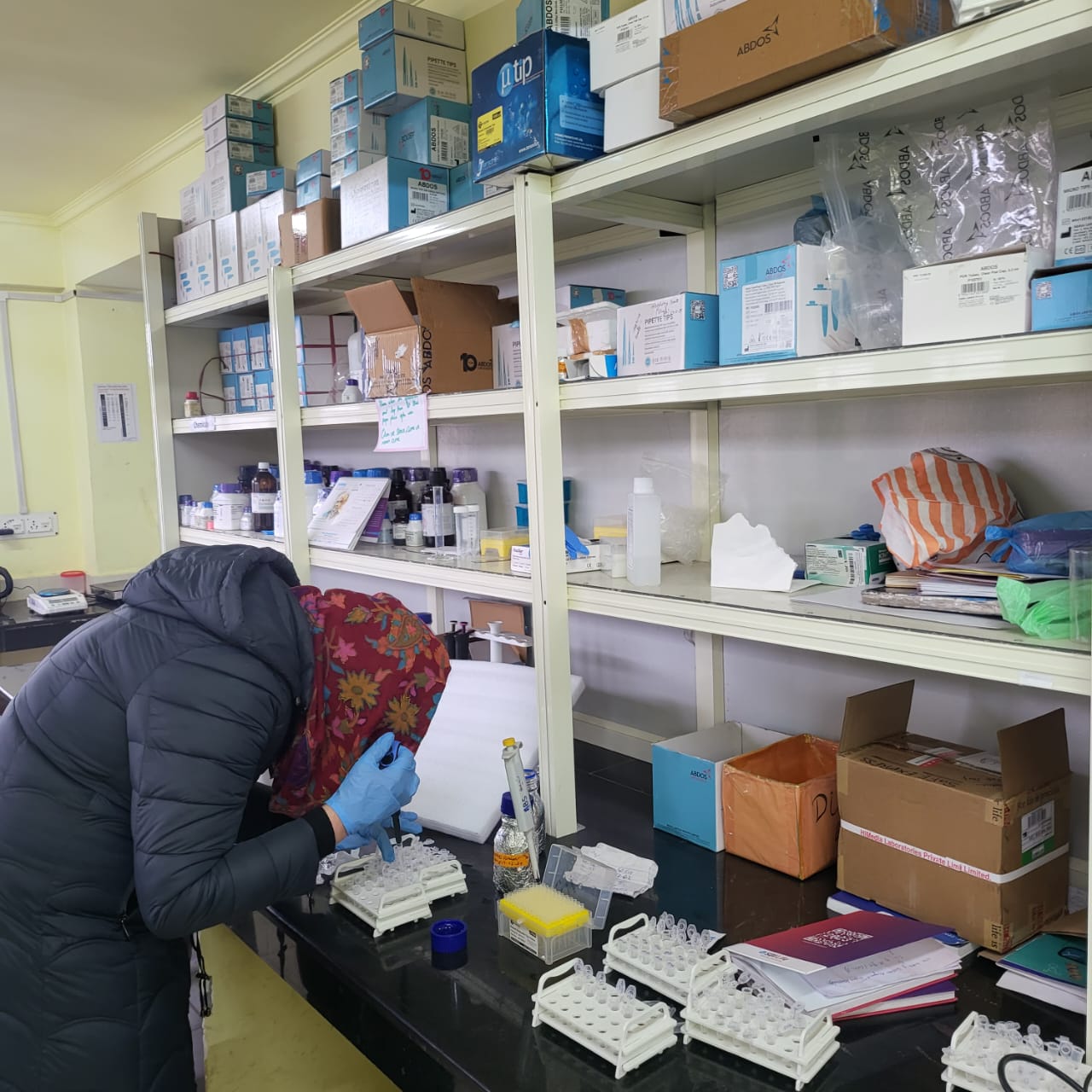

Molecular Breeding Laboratory
The Molecular Breeding Laboratory is a specialized facility dedicated to advancing fodder crop genetics and breeding, with focus on maize, sorghum, alfalfa, and forage legumes. The lab supports trait discovery, marker development, and genomic-assisted breeding to enhance biomass yield, nutritional quality, and stress resilience. Equipped for DNA extraction, PCR-based genotyping, and analysis of next-generation sequencing data, the laboratory enables rapid, science-driven improvement of fodder crops for sustainable livestock productivity and regional fodder security.

