All R&D Activities
A collective overview of scientific interventions, outcomes, and innovations across all 29 projects.
Total Activities
73
Across All Projects
Active Projects
10
Contributing Research
Top Projects by R&D Output
Top 10
Production of Foundation Seed
Supply of Foundation Seed to all the KVKs for Seed Production
Augment FS production of Dept of Agri

Production of Breeders Seed
Production of sufficient quantities of Breeders/Foundation/Certified Seed for all the crops involved in Seed Chain to improve SRR to 33% (SP), 50% (CP) and 100% in hybrids
Conduct of OFT'S for Shallot
A total of 60 On-Farm Trials (OFTs) were conducted from 2023 to November 2025 to evaluate improved varieties and production technologies of niche crops under farmers’ field conditions, facilitating performance assessment, refinement, and wider adoption.
Devising package of practices for Shallot
Two research trails were laid during 2024-25
entitled
1. "Effect of Nutrient Management & Crop Geometry on growth & Yield of Shallot.
2. "Impact of Planting Dates & Bulb Size on Growth & Yield of Shallot (Kashmiri Pran)

Standardization of Production Technology of Niche crops
Production Technology of Saffron, Kalazeera, Mushkbudji, Red Rice Chilli & Shallot are at final stage for release of GAP
Development of markers of Niche crops & seeking of GI Tag
DUS characterization of niche crops is under progress to establish their unique varietal traits. GI tags have been granted to Saffron and Mushkbudji, while applications for Kalazeera, Shallot, Kashmiri Chilli, and Red Rice have been submitted.
Collection and evaluation of germplasm
A total of 162 number of accessions were collected & are under evaluation for varietal development

Standardization of package of practices for natural farming in vegetable crops
Standardization of the package of practices for natural farming in vegetable crops is carried out to develop scientifically validated, location-specific production protocols that ensure sustainable yields without reliance on synthetic inputs.

Varietal / Hybrid Development
Varietal and hybrid development in vegetable crops is undertaken to improve yield potential, quality, and adaptability to diverse agro-climatic conditions. The main objective is to develop varieties and hybrids that are resistant or tolerant to major diseases, insect pests, and abiotic stresses such as heat, cold, drought, and salinity. This process also focuses on enhancing nutritional quality, shelf life, uniformity, and market acceptability. Ultimately, varietal and hybrid development ensures the availability of high-performing, climate-resilient vegetable cultivars that increase productivity, reduce input costs, and improve the livelihood of farmers.

On Farm Trials (OFTs)
Low productivity of vegetable crops in the Valley is largely attributed to the use of low-yielding local cultivars and adoption of non-scientific cultural practices by farmers. Traditional varieties are often susceptible to diseases and insect pests, while practices such as blanket input application, broadcasting of seed, improper spacing, and uncontrolled irrigation further reduce yields. Adoption of recommended high-yielding varieties along with the scientific package of practices—such as line sowing or transplanting, proper crop geometry, balanced use of manures and fertilizers, timely intercultural operations, and regulated irrigation—can substantially improve productivity, crop health, and farmers’ income across vegetable crops.

Walnut Outlook
The report provides a comprehensive analysis of the walnut industry, with a focus on Kashmir and the global scenario. The document highlights China as the leading world producer and the UT of Jammu and Kashmir as India's largest producer, with Anantnag consistently holding the largest cultivation area in Kashmir. It details various walnut varieties with their characteristics, such as WONTH and KAGAZI, outlines the J&K walnut season, with harvest typically from October to November, and includes market statistics on walnut arrivals, average prices (2012-2023), and export data (2014-15 to 2021-22).

Cherry Outlook
This report provides a nuanced analysis of the cherry market dynamics, a crop of paramount importance in Jammu and Kashmir and widely traded across major terminal markets in India. It details the importance of J&K as a key player in the cherry landscape, annually producing around 7,000 metric tons of varieties such as Shalimar and Makhmali. Furthermore, the document presents information on global cherry varieties, the cherry season in J&K, key production statistics (with Ganderbal as a leading district), India's contribution to global production, and an overview of the global cherry trade.

Apple Outlook
This report provides a detailed market intelligence overview of the apple industry. The analysis encompasses the global market, noting a total production of 84.00 million metric tons (MMT) with China as the principal producer, and projects the global market valuation to reach USD 103.4 billion by 2033. The report further segments the findings to detail the Indian market, estimating a domestic production of 2.55 MMT and significant fresh apple imports of 6.0 MMT. A focused sectoral overview is provided for Jammu & Kashmir, which details its 2.06 MMT production, highlights key contributing districts such as Baramulla and Shopian, and includes an analysis of monthly average prices across various market-variety segments and the critical role of Controlled-Atmosphere (CA) storage.

Market Intelligence Report (Cherry) - 2025-26
The Market Intelligence Report (MIC) on Cherry for 2025-26, prepared by the Market Intelligence Cell of Sher-e-Kashmir University of Agricultural Sciences and Technology of Kashmir, focuses on revitalizing the Kashmir cherry industry as a strategic economic opportunity to reduce import dependency and boost farmer livelihoods. The report outlines strategic objectives such as reducing imports by 30%, improving yield, firmness, and shelf life, strengthening the cold chain, and establishing a premium Kashmiri Cherry Brand; these goals are set against key challenges including varietal obsolescence and significant post-harvest losses of up to 30%. To address these issues, the recommended strategic interventions involve varietal advancement, promoting High-Density Planting (HDP), and establishing Controlled Atmosphere (CA) storage facilities. Furthermore, the document provides an economic viability analysis for cherry cultivation in District Shopian and District Srinagar, alongside a market price forecast for Makhmali and Mishri varieties in the Azadpur market.

Market Intelligence Report (Apple) - 2025-26
This document is the Market Intelligence Report on APPLE for 2025-26, developed by the Market Intelligence Cell (MIC) to enhance data-driven decision-making within the agricultural supply chain in Jammu and Kashmir. The report provides a comprehensive analysis of apple price dynamics—covering market, variety, and grade—and establishes a robust price forecasting system. This system is built upon the highly effective LSTM (Long Short-Term Memory) model, which was selected for its superior accuracy in predicting market fluctuations compared to traditional methods. By providing this strategic foresight, the report aims to significantly improve operational efficiency and foster greater income stability for farmers.

Survey, collection and conservation of priority MAP species at Germplasm bank of Faculty of Forestry- SKUAST-K
Collection and conservation of priority MAPs species (Saussurea costus, Picrorhiza kurroa, Valeriana jatamansi, Thymus linearis, Tagetes minuta, Salvia rosmarinus, and Inula racemosa ) from different locations across Kashmir Valley to strengthen genetic resource management and support high-quality raw material production in Jammu & Kashmir.

Molecular and Chemoprofiling of priority species of MAPs
Molecular authentication, qualitative/quantitative phytochemical evaluation and bioactivity assessment of prioritized MAP species.
R & D Activities of the Project: 1. Establishment of Bee Breeding Centre (BBC) for Climate-Smart Bee. 2. Establishment of Disease Diagnostic & Quarantine Centre. 3. Development of Quality Nucleus Stock Centres
Description:
Activity 1 : A sensor-based Open Top Chamber (OTC) system is being developed to breed climate-smart honey bees. Colonies are screened for heritable traits such as high honey yield, disease tolerance, cold tolerance, and overall performance. Superior colonies are selected, and queen multiplication is initiated to develop resilient bee lines. Activity 2: A dedicated centre is being set up for diagnosing honey bee pests and diseases using visual inspection, microscopic examination, and molecular techniques. The quarantine facility helps restrict disease spread and ensures healthier beekeeping operations. Activity 3 : Quality Nucleus Stock Centres are being established to maintain and multiply superior honey bee genetic resources. Controlled breeding and evaluation ensure the development of strong, productive, and disease-resistant colonies for wider dissemination.

Project Progress
80% of the civil work completed
34 exotic silkworm genotypes procured to enrich Germplasm Bank
30 breeding lines isolated for breed development
Establishment of Silkworm Crop Improvement Laboratory
R&D for Establishment of Silkworm Crop Improvement Laboratory for the development of new silkworm breeds/ hybrids

Development and evaluation of live earthworm Vermicompost Separator
The live earthworm vermicompost separator developed is a mechanised system designed to efficiently separate live earthworms from mature vermicompost without causing injury or mortality to the worms. The machine aims to reduce labour intensity, separation time, and dependence on traditional manual or sun-drying methods, while ensuring high recovery of healthy earthworms for reuse in vermicomposting units.

Design and Development of a self propelled rover for NPK monitoring
The self-propelled rover developed for NPK (Nitrogen, Phosphorus, and Potassium) monitoring is an autonomous/semiautonomous ground-based sensing platform designed for real-time, site-specific soil nutrient assessment in agricultural fields. The system aims to support precision nutrient management by reducing reliance on conventional laboratory soil testing and enabling rapid spatial mapping of soil fertility.

Design and Development of a Tractor Operated Walnut Harvester.
The tractor-operated walnut harvester developed by me is a mechanised system designed to improve the efficiency, timeliness, and labour economy of walnut harvesting under Indian orchard conditions, particularly in hilly and temperate regions. The machine is mounted on a standard agricultural tractor and utilises the tractor’s power take-off (PTO) and hydraulic system as the primary power sources, thereby eliminating the need for an independent power unit.

R&D (Establishment of Prototype production centre for design and development of region-specific farm machinery)
Establishment of Farm Machinery Prototype Production Centre shall help in design and development of region specific farm equipment/machines which are not commercially available.

Introduction & promotion of new high yielding strains.
Available strains of High value mushroom obtained from various sources to test their performance on locally available substrates under Kashmir conditions.

Cluster demonstrations
front line demonstrations will greatly increase the seed replacement rate and varietal replacement rate in oilseed thereby increasing production and productivity of the crop
Quality seed production
12.5q breeder seed production of all released/indented oilseed varieties from kashmir.
125q foundation seed production of all indented oilseed varieties from kashmir.
varietal evaluation trials on brown sarson, Gobhi sarson, sunflower and soyabean.
50 research trials on rapeseed mustard and other oilseed crops
varietal development with production technology
Development of 2 varieties of brown sarson and one variety of Gobhi sarson.
Development of full package and practices for newly developed varieties.
Standardisation and Demonstration of IFS units per district of Kashmir valley
Standardization and Demonstration of Integrated Farming Systems (IFS) in Kashmir Valley involves adapting and promoting diverse, location-specific IFS farming models suitable to the agro-climatic conditions of Kashmir to integrate crops, horticulture, livestock and allied activities to ensure efficient resource use, higher productivity, diversified income and sustainability improving livelihoods of small and marginal farmers

Centre of Excellence on Integrated Farming System
It is a research, training, and demonstration hub that develops and promotes sustainable agricultural models combining various farm enterprises like crops, livestock, aquaculture, and agroforestry to improve farm productivity, profitability, and environmental sustainability, particularly for small and marginal farmers.

Standardisation of efficient and reproducible tissue culture protocols for ornamental crops like Orchids, Gypsophila, Scented Geranium, Loropetalum, Scented Verbena—and to initiate mutation studies in Lisianthus
Optimisation of sterilisation, explant selection, and media formulation for high-frequency shoot proliferation
Rooting, acclimatisation, and hardening protocols for enhanced field survivability
mutation induction studies in Lisianthus

Pacakage of Practices developed for Maize , Pulses and Potential crops
10 package of practices developed for Maize pulses and potential crops.
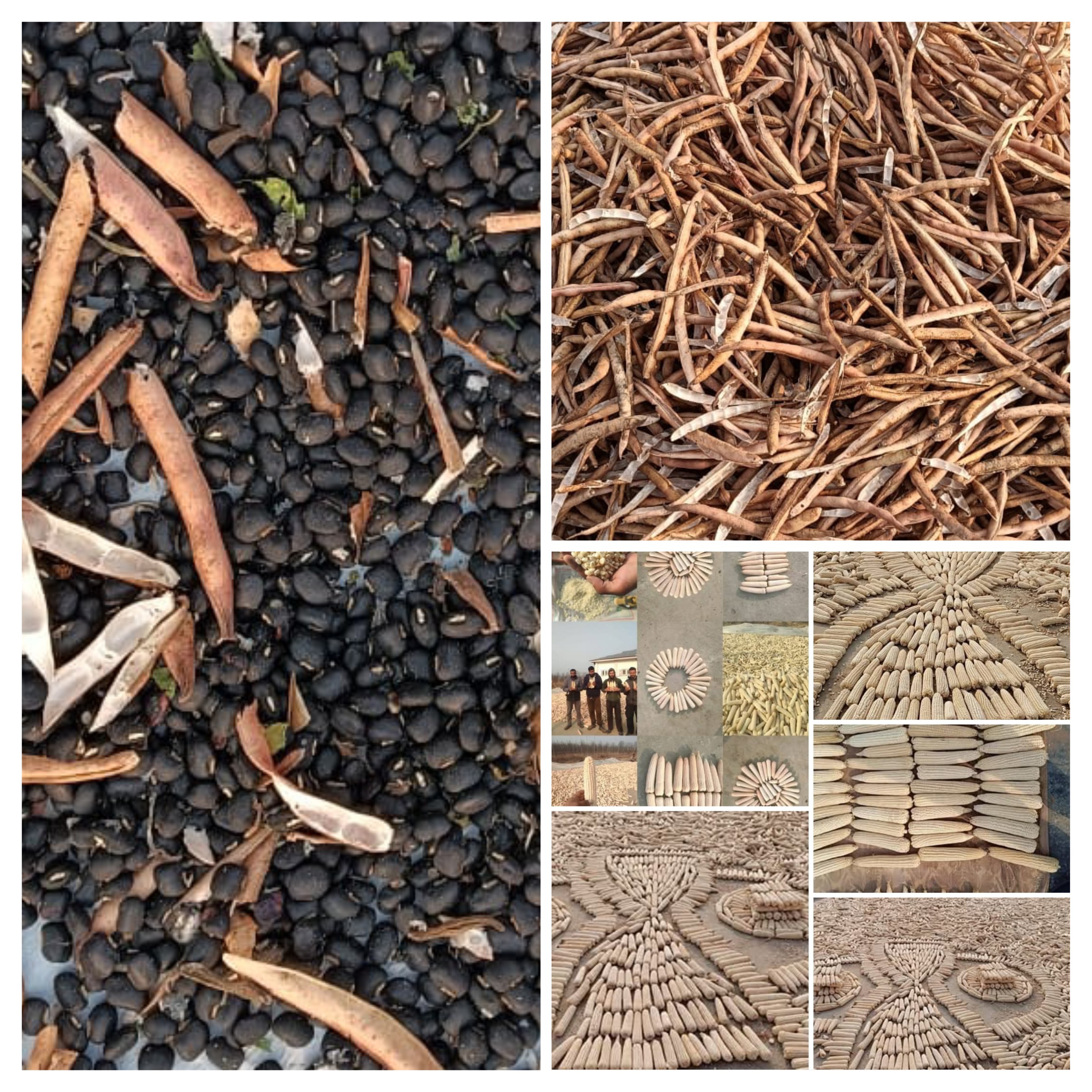

Seed Production of climate resilient crop varieties
500 quintal seed of climate resilient and nutritionally dense maize, forage and pulse varieties produced and deployed in Rainfed Niches

Scholarly Research Utilization of Project developed lab facilities
16 students 10 MSc and 6 PhD scholars utilized the laboratory facilities to conduct physiological, biochemical, root architecture (drought tolerance), and soil physical-chemical analyses for their research.

Resource Mapping
Resource mapping for 250 sites under rainfed ecology

Crop Diversifcation
crop demonstrations to enhance economic and nutritional security in rainfed ecologies.

Climate smart and Nutritionally enriched varities.
24 climate smart and nutritionally enriched varieties released at national and state levels
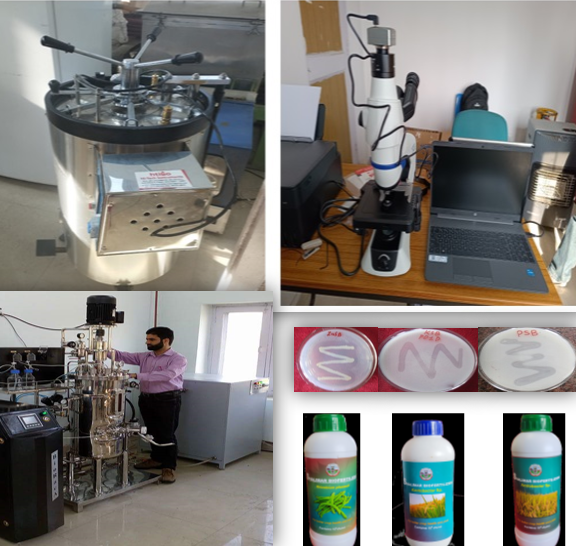

Screening of Temperate Strains of Microbes
•Collected samples from locations across all districts of Kashmir Valley
•Isolated and characterized more than 300 microbial isolates for their efficiency as bio-fertilizers (mineral solubilizers/N-fixers, etc.)
•Selected microbial strains on basis of qualitative and quantitative screening for development of formulations. Developed & disseminated more than 12 products/technologies among farmers .
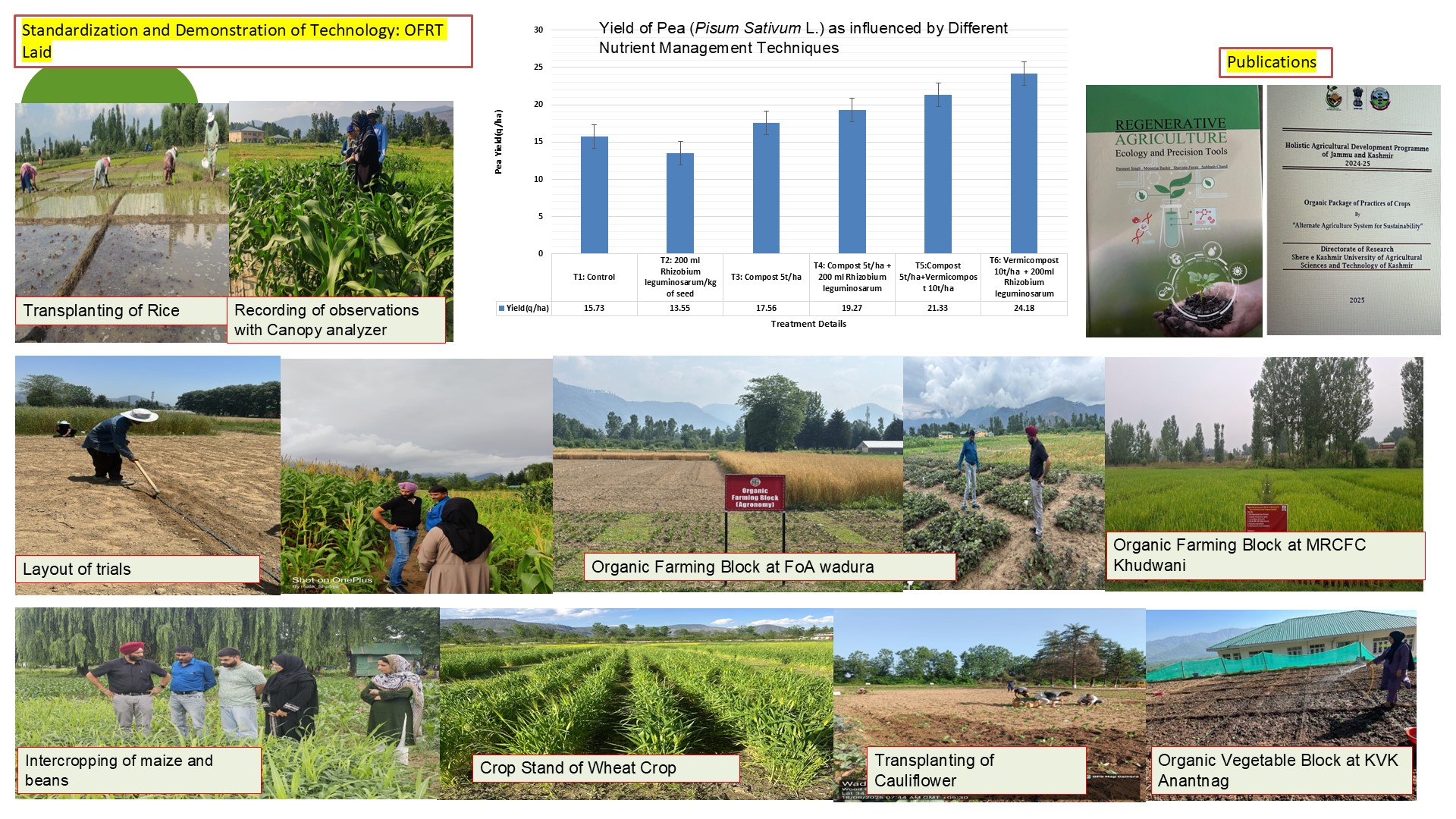
On Farm Research Trials
On-farm research trials are experiments conducted directly on farmers’ fields, rather than in controlled research stations that aim to evaluate and adapt organic farming technologies (such as composting, biofertilizers, crop rotations, and natural pest control) under real-world conditions.

strengten of Biological controls labs
Bio-control agents(BCAs) like bacteria, fungi, viruses, insect predators or parasitoids,
botanicals and plant growth promoting rhizobacteria (PGPR) have very important role in
reducing pest use.

PHI ESTIMATION
Validated Pre harvest interval of 30 pesticides on apple for maintaining standard MRL Value

development and validation of decision support system for 3 diseases and 3 pests of apple
Deployment of location specific/weather based Decision support system
for real time/need based advisory to farmers.
Bio-fabrication of metal Nano-formulations for apple crop disease and health management
This study focuses on the green (bio-based) synthesis of metal nano-formulations using plant extracts or microbial systems for sustainable disease and health management in apple. Bio-fabricated metal nanoparticles offer targeted antimicrobial activity, improved nutrient use efficiency, and reduced chemical load, aligning with eco-friendly and precision horticulture approaches.
Development of certification protocols
This initiative focuses on developing standardized, science-based certification protocols to ensure the quality, genetic purity, phytosanitary status, and traceability of planting material/produce. Such protocols support uniformity, authenticity, and compliance with national and international standards, thereby strengthening nursery systems, value chains, and stakeholder confidence.
To assess the dynamics of Apple progeny through multi-omics approach
This study aims to understand the biological and genetic dynamics of apple progeny by integrating multi-omics tools such as genomics, transcriptomics, proteomics, and metabolomics. The approach enables comprehensive insight into trait inheritance, growth, development, stress response, fruit quality, and disease resistance, thereby accelerating precision breeding in apple.
Characterization and Evaluation of Walnut (Juglans regia L.) Germplasm of Diverse Origin
The study focuses on systematic characterization and evaluation of walnut germplasm collected from diverse eco-geographical regions to assess variability in morphological, phenological, nut, and kernel traits. Such evaluation helps in identifying elite genotypes with superior yield, nut quality, adaptability, and stress tolerance for use in breeding and conservation programmes.
Hydroponic strawberry culture for vertical expansion
Hydroponic strawberry culture under vertical farming systems involves growing strawberries without soil using nutrient solutions in stacked structures (towers, racks, A-frames, or vertical columns). This approach maximizes space use, improves resource efficiency, and enables year-round production under protected environments (polyhouse/greenhouse), making it suitable for urban, peri-urban, and land-limited regions.
Apple twig vs. Walnut shell Biochar: Exploring Biological Properties and Carbon-Nitrogen Dynamics in Acid and Alkaline Soils
Biochar application is a promising strategy for improving soil health and enhancing carbon sequestration. Apple twigs and walnut shells, abundantly available horticultural residues, differ in their lignocellulosic composition and pyrolysis behavior, which may influence biochar properties and soil responses. This activity focuses on evaluating the impact of these two biochar types on soil microbial activity, organic carbon stabilization, nitrogen mineralization–immobilization processes, and overall soil fertility in acidic and alkaline soils. Understanding these interactions will help optimize biochar selection and application for site-specific soil management.
Evaluation of training systems in Cherry
Cherry productivity and fruit quality are strongly influenced by tree architecture and training system. Traditional open or spreading systems often result in excessive vigour, poor light distribution, and delayed bearing. Evaluation of modern training systems such as central leader, spindle, KGB (Kym Green Bush), UFO (Upright Fruiting Offshoots), and steep leader aims to improve early bearing, fruit quality, and labour efficiency. This activity involves systematic evaluation of growth, yield, fruit quality parameters, and ease of orchard management under local agro-climatic conditions.
Identification elite cultivars of Nakh pear
Nakh pear is an important temperate fruit valued for its crisp texture, juiciness, and market demand. However, wide variability exists among available cultivars in terms of yield, fruit quality, maturity period, and adaptability. Identification of elite Nakh pear cultivars involves multi-year evaluation of available germplasm for growth, bearing behaviour, yield efficiency, fruit quality attributes, and tolerance to biotic and abiotic stresses. The objective is to recommend superior cultivars suited to specific agro-climatic conditions
Development of Self-fertile varieties of almond
Most traditional almond cultivars are self-incompatible and require compatible pollinizers and adequate bee activity for fruit set, making production highly dependent on orchard design and pollination management. Development of self-fertile almond varieties aims to ensure reliable fruit set, stable yields, and simplified orchard management. The program focuses on incorporating self-compatibility traits into elite germplasm while maintaining high nut quality, productivity, and tolerance to climatic stresses.
Seedless cultivar development in grape
Seedlessness is one of the most desirable traits in table grapes due to high consumer preference and export demand. Development of seedless grape cultivars focuses on exploiting stenospermocarpy and parthenocarpy, supported by techniques such as embryo rescue to recover viable progenies. The program involves selection of elite seedless genotypes, evaluation for yield, berry size, bunch characteristics, quality attributes, and resistance to biotic and abiotic stresses.
Development of lateral bearing cultivars of walnut
Traditional walnut cultivars predominantly bear fruit on terminal shoots, resulting in late bearing and low yield efficiency. Lateral-bearing walnut cultivars produce female flowers on lateral buds, leading to early bearing, higher productivity, and more uniform yields. Development of such cultivars is essential for improving orchard profitability, optimizing high-density planting systems, and meeting increasing market demand for quality walnuts. This program involves selection of lateral-bearing genotypes, assessment of yield, nut and kernel quality, and adaptability to local climatic conditions.
Development of new scab resistant apple varieties
Apple scab is one of the most destructive diseases of apple, causing severe yield and quality losses and necessitating repeated fungicide applications. The development of scab-resistant apple varieties aims to reduce chemical dependency, production costs, and environmental risks. This activity involves identification of resistant sources, hybridization with elite cultivars, selection of resistant progenies using phenotypic and molecular tools, and evaluation for horticultural and quality traits suited to local agro-climatic conditions.
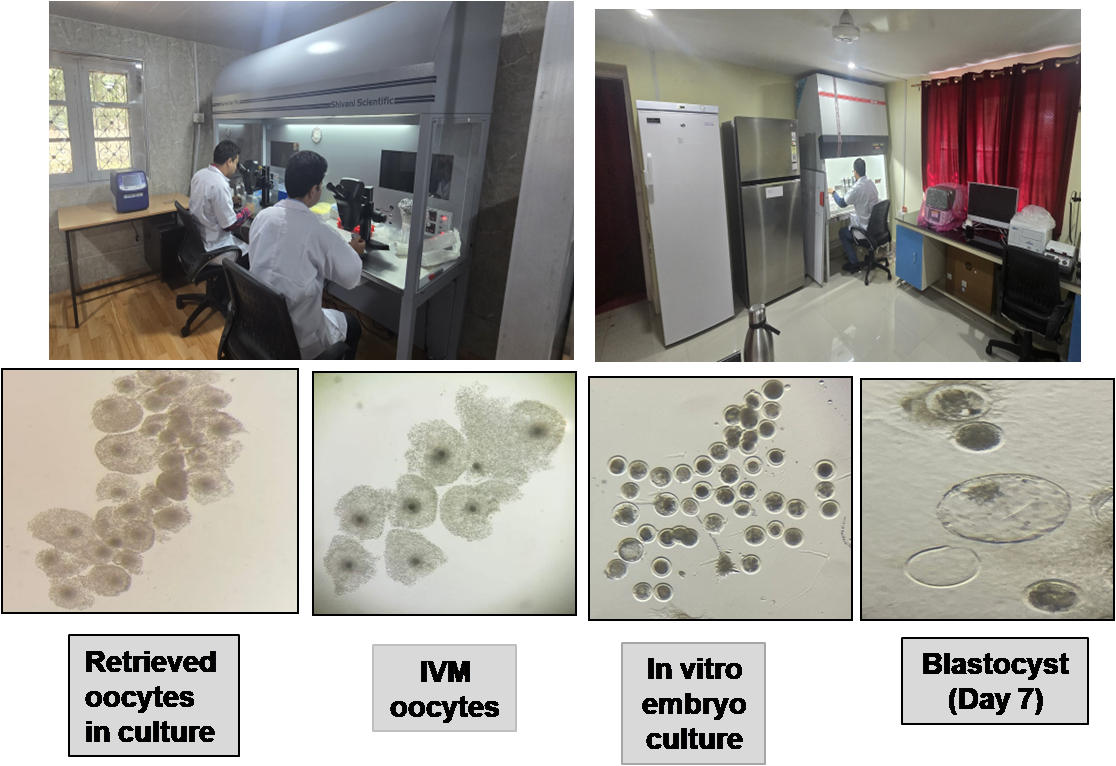

1. Standardization of in vitro embryo production
Procedures for in vitro embryo production through In vitro fertilization using frozen thawed semen have been standardized
Metagenomic studies of sheep rumen microbiomeof Texal sheep
Strong correlations exist between specific microbial groups (markers) and rumen metabolites (like succinic acid), impacting host performance and adaptation .Using microbial biomarkers to understand disease resistance and environmental adaptation .The fecal samples will be collected from the sheep to study rumen microbiome
Evaluation of newly imported Texal Sheep
Performance/adaptation
studies of the breed in organized sectors of Government sheep breeding farms
HADP Code 25: Roadmap for Poultry Development in J&K (2025-26)
1. Variety development
• Development of egg-type variety for backyard poultry rearing
• Evaluation of F1 cross of K.F. × Exotic layer selection
• Interse mating of selected F1 parents
2. Poultry Housing
• Designing of poultry housing models for backyard poultry
3. Waste to wealth
• Formulation of protocol for poultry waste management
4. Feed formulation
• Civil works for the feed mill and procurement of machinery for the feed mill & equipment for the nutrition laboratory.
5. Vaccine Development
• Sero-prevalence studies, identification of vaccine candidates.
6. Poultry Disease Diagnosis
• Development of poultry diagnostic procedures
• Evaluation of antibiotic alternatives
Capacity Building
Capacity building in fisheries aims to improve both the technical and human capabilities required for sustainable fisheries development and responsible stewardship of aquatic ecosystems.

Value addition and product development.
In Jammu and Kashmir mostly due to climatic conditions people consume a lot of animal protein in different forms, it is necessary to add value to the fishes produced so that more employment is generated and more fish products are formed and people will have enough choices for selection of these varied fish products.

Disease diagnosis & prophylaxis.
A large proportion of the population of the fishes starting from the eyed stage to brooders is lost due to certain diseases out breaks, therefore in order to control this loss, a disease diagnostic and Health management needs to be taken.

Genetic interventions for growth and breeding in cold water fishes
The Trout fish grows to table size in eighteen months and the breeding period is short mainly from November to February. This short breeding period leads to the saleable fish in one particular period while in other periods we don’t have enough saleable biomass. Likewise if the growth of the fish is reduced from eighteen months to fourteen or twelve months, the production of the fish will increase many folds.

Development of low cost feed
The ingredients of the Trout Fish feed are mostly imported from the maritime states of India and that is the reason of high cost of the feed. As a result a good amount of the earning of the farmer goes on feed cost.
The Division of Fish Nutrition and Biochemistry (FNB), Faculty of Fisheries, SKUAST-K is undertaking this research programmes for the development, demonstration and commercialization of cost effective fish feed technology from the locally available ingredients for coldwater aquaculture.
.jpeg)
Identification of Constraints and Development of Sustainable Value Processing Modules for wool Industry.
The envisaged activity focuses on a comprehensive assessment of the wool industry to identify critical constraints that limit its productivity, profitability, and sustainability. These constraints may include variability in wool quality, inadequate processing technologies, high production costs, inefficient waste management practices, limited adoption of eco-friendly technologies, and challenges in value addition, product diversification, and market access.
Following the identification and analysis of these constraints, the study aims to design and develop sustainable value processing modules tailored to different stages of the wool value chain from raw wool handling and scouring to processing, finishing, and by-product utilization.
The proposed sustainable processing modules are intended to improve product quality, expand the range of value-added wool products, enhance economic returns for producers and processors, and minimize environmental impacts. Overall, the study seeks to support the transformation of the wool industry into a more resilient, environmentally responsible, and economically viable sector, contributing to sustainable industrial growth and rural livelihood development.
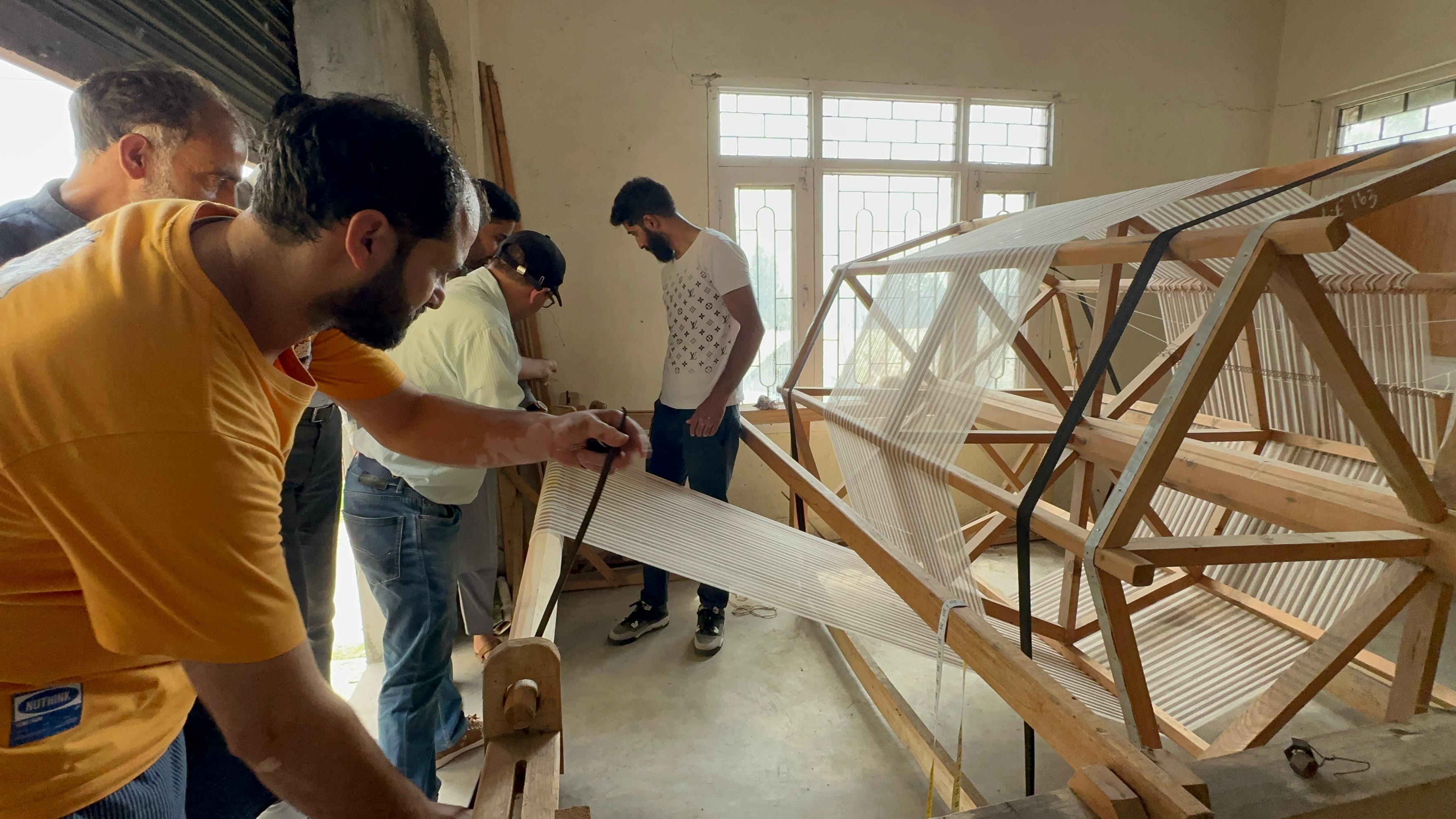

Revival of wool and fur based cottage industry
The revival of the wool and fur–based cottage industry is essential for preserving traditional craftsmanship, generating rural employment and strengthening local economies. This revival can be achieved by focusing on improving access to quality raw materials, introducing modern and affordable tools, and upgrading traditional skills through targeted skill upgradation programmes. By integrating indigenous techniques with contemporary designs and sustainable practices, artisans can produce market-relevant products while maintaining cultural identity. Strengthening cooperatives, improving credit and insurance support, and facilitating marketing through exhibitions, and digital platforms, further enhance income opportunities.
Under the project, the revival has been envisaged through the Handholding and technology support to the artisan communities. This approach shall strengthen traditional livelihoods while enabling artisans to adapt to changing market demands. Key initiatives include identifying beneficiaries, forming or supporting cooperative societies and self-help groups, and providing processing tools such as tabletop paddle-operated charkhas, handlooms, carpet looms, and warping systems to enhance productivity and reduce physical drudgery. This shall be complemented by skill upgradation programmes focusing on enhancing traditional skills and introducing modern techniques in wool spinning, warping, weaving, dyeing, and finishing besides enhancing the skill for contemporary designs, color combinations, quality control, and product diversification. The artisans shall be further supported in branding, packaging, and labeling to enhance product appeal and marketing through exhibitions, expos, and digital platforms.
Development of wool and fur based value added products
This activity focuses on transforming raw wool and fur into high-quality, value-added products that meet industry and consumer demands. It involves designing and developing innovative products through processes such as blending, carding, felting, knitting, weaving, finishing, and dyeing. By leveraging modern processing techniques and traditional craftsmanship, the activity aims to enhance the functional and aesthetic qualities of wool and fur products, including textiles, garments, home décor, accessories, and specialty items.
The initiative not only adds economic value to raw fibres but also promotes entrepreneurship, supports artisan communities, and contributes to the sustainable growth of the regional wool and fur industry. It serves as a platform for research, innovation, skill development, and commercialization of premium animal-fibre-based products.
Establishment of Fur Processing Unit
Sheep slaughtering, in addition to supplying mutton, generates a substantial volume of high-value by-products that often go unaccounted for in economic evaluations. Among these, sheep skins are particularly important, comprising nearly 7–11% of the animal’s live weight. Despite their significant market potential, these skins remain largely underutilized, resulting in considerable revenue losses that could otherwise support rural livelihoods and strengthen the livestock value chain.
In the Union Territory of Jammu & Kashmir, an estimated 5,000–6,000 pelts are produced each day. However, due to the absence of a dedicated processing and value-addition industry, most of these pelts are discarded, allowed to deteriorate, or sold at nominal prices. This leads to the wastage of a resource with high commercial value and limits income-generating opportunities for local communities. Systematic collection, proper grading, and scientific processing into premium fur and leather products could multiply their market value manyfold. Such value addition has the potential to revive Kashmir’s once-flourishing fur industry, renowned historically for its exceptional craftsmanship.
The establishment of a fur processing unit will not only introduce environmentally friendly and modern pelt-processing technologies but also serve as a centre for capacity building, incubation, and entrepreneurial demonstration. This facility can play a pivotal role in developing skilled human resources, fostering innovation, supporting startups, and creating sustainable livelihood opportunities in the region.
Upgradation of Animal Fibre Quality Assurance Laboratory
India is home to a rich diversity of livestock, including sheep, with 42 recognized breeds distributed across various agro-climatic regions, collectively producing about 45.10 million kilograms of wool annually. The Union Territory of Jammu & Kashmir contributes significantly to this sector, yielding 7.53 million kilograms of some of the finest quality wool in the country. In addition to wool, India also produces several specialty animal fibres derived from goats, rabbits, and camels—renowned for their superior fineness, lustre, warmth, softness, elegance, and aesthetic appeal. Among these, Pashmina stands out as a premium luxury fibre, celebrated both nationally and internationally.
Despite this rich resource base, the accurate assessment of raw animal fibres and their value-added products remains crucial for determining marketability and end-use potential. A persistent limitation in the fibre sector has been the lack of awareness and access to reliable quality testing facilities, which directly impacts the income, confidence, and market opportunities of stakeholders. Consequently, establishing a dedicated, credible quality assurance facility has become essential to ensure the sustainable development and global competitiveness of India’s animal fibre industry.
In this context, Sher-e-Kashmir University of Agricultural Sciences and Technology of Kashmir (SKUAST-K), as an innovation-driven farm university, has established a Centre of Excellence (CoE) on fibre testing entitled “Animal Fiber Quality Assurance Laboratory” at FVSc & AH, Shuhama. The facility has been created with the support of the Government of J&K under the HADP project “Promotion of Wool and Pelt for Effective Processing and Marketing.”
Accreditation of Animal Fibre Quality Assurance Laboratory
The University intends to obtain NABL accreditation for its Animal Fibre Quality Assurance Laboratory in compliance with ISO/IEC 17025 standards, with the objective of ensuring high standards of quality, accuracy, and reliability in testing and analysis of animal fibres such as wool, pashmina and other specialty fibres.
NABL accreditation will establish the laboratory’s technical competence through standardized testing protocols, validated methodologies, calibrated equipment, and a robust quality management system.
Accreditation will enhance the credibility and national/international acceptance of test reports generated by the laboratory, thereby supporting research, industry, exporters, entrepreneurs, and artisans associated with the animal fibre sector. It will also facilitate effective quality control, grading, and certification of fibres, leading to improved marketability and value realization. Further, the accredited laboratory will serve as a centre for capacity building, training, and technology dissemination, contributing to sustainable development of the animal fibre value chain and strengthening stakeholder confidence in quality assurance services.

Hydroponics Fodder
To work out the Suitability of different Fodder Crops under Hydroponics systems

Varietal Development: Legume Fodders
Varietal Development: Legume Fodders (Annual, Perennial)

Varietal Development
Varietal Development: Cereal Fodders (Annual, Perennial)

